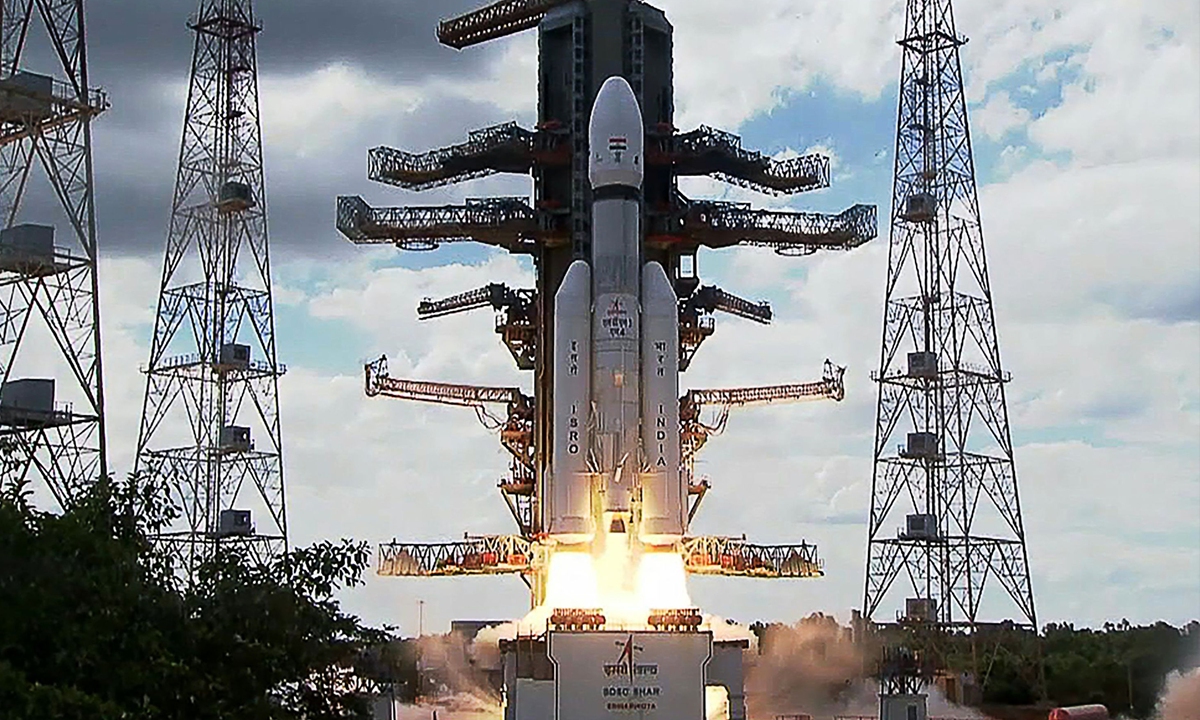
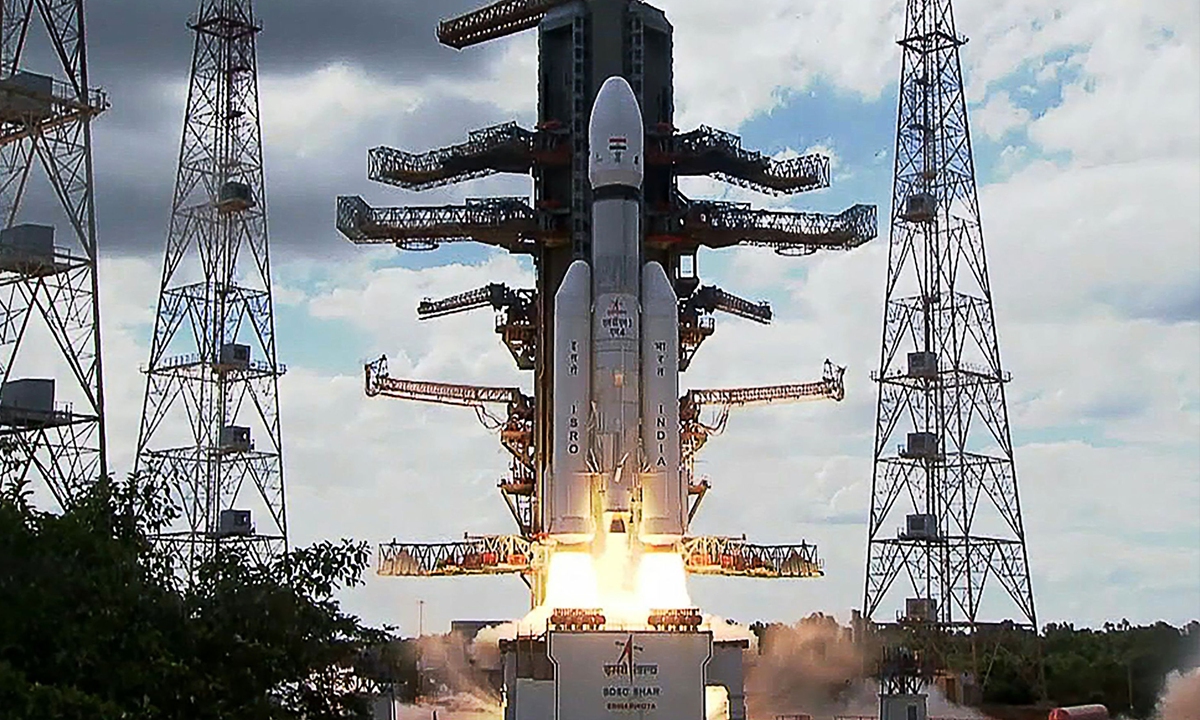
China has unveiled Zuchongzhi-3, a 105-qubit quantum processor that works 10¹⁵ times faster than top supercomputers. This device is now among the world's most powerful quantum computers.
For comparison, Google's 53-qubit Sycamore processor made headlines in 2019 by completing a task in minutes that would take traditional supercomputers thousands of years. Zuchongzhi-3 demonstrated its power by handling an 83-qubit, 32-layer random circuit sampling task.
This development signals China's growing leadership in quantum computing technology.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General USA vs China 14-March-2025 by east is risingSOMTOM
Chinese company Monica has released Manus, a "general AI agent" designed to operate autonomously on complex tasks, according to recent industry reports. Unlike conventional AI systems that provide information, Manus can reportedly execute complete multi-step tasks independently, such as building websites or creating lesson plans, and continues working even when users disconnect. The system has performed strongly against benchmark tests, outperforming some Western AI models in certain evaluations. Technology analysts note this represents another significant development in China's rapidly advancing AI sector.
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General USA vs China 12-March-2025 by east is risingচীনা শিল্প নীতি দক্ষতার সাথে রাষ্ট্রীয় নির্দেশনা এবং বাজার ব্যবস্থার সংমিশ্রণ ঘটায়। রাষ্ট্র-সমর্থন এবং বাজার-বাহিনীর মধ্যে সীমারেখা আরও অস্পষ্ট করে বেইজিং অর্থনৈতিক অংশীদারদের জন্য বিভিন্ন ধরনের ভর্তুকি মূল্যায়ন করা আরও কঠিন করে তুলেছে।
জার্মানির গোপন চ্যাম্পিয়নদের (জার্মান শিল্পোৎপাদন প্রচণ্ডভাবে ছোট মাঝারি শিল্প প্রতিষ্ঠানগুলোর ওপর নির্ভর করে যাদের নাম সাধারণভাবে অজানা আর এদেরই গোপন চ্যাম্পিয়ন বলা হয়) দেখে অনুপ্রাণিত হয়ে, চীনা থিঙ্ক ট্যাঙ্ক এবং বিনিয়োগ ব্যাংকিং নথিগুলি জার্মান গোপন চ্যাম্প-দের অনুকরণ করার জন্য একটি মডেল হিসেবে বিবেচনা করে। জার্মান গোপন চ্যাম্পিয়ন ধারণাটি জার্মান ব্যবস্থাপনা তাত্ত্বিক এবং পরামর্শদাতা হারমান সাইমন বিশ্ব বাজারে জার্মান ছোট ও মাঝারি শিল্প-এর সাফল্য ব্যাখ্যা করার জন্য তৈরি করেছেন। এই সংস্থাগুলি জার্মানিতে বর্তমান অর্থনৈতিক ও সামাজিক পরিস্থিতি থেকে আবির্ভূত হয়েছিল, যেমন চমৎকার বৃত্তিমূলক প্রশিক্ষণ, সামাজিক ব্যাঙ্কগুলির সাথে ঘনিষ্ঠ সম্পর্ক এবং একটি স্বতন্ত্র কর্পোরেট সংস্কৃতি। বেইজিং মনে করে যে এটি রাষ্ট্রীয় হস্তক্ষেপের মাধ্যমে তাদের সাফল্যের প্রতিলিপি তৈরি করতে পারে। চীনের খুব ভিন্ন সামাজিক ও অর্থনৈতিক পরিবেশের অর্থ হল স্থানীয় গোপন চ্যাম্পিয়নদের উত্থানের আয়োজন করা সরকারী কর্মকর্তাদের উপর নির্ভর করে।
উচ্চ প্রযুক্তির ক্ষুদ্র ও মাঝারি আকারের উদ্যোগগুলি চীনের শিল্প নীতিতে মূল নতুন খেলোয়াড় হিসাবে আবির্ভূত হয়েছেঃ তাদের বাজারে বিশেষজ্ঞ হওয়ার, বিদেশী আমদানীর দেশীয় বিকল্প তৈরি করার এবং চীনের শিল্প শৃঙ্খলকে শক্তিশালী করার সম্ভাবনা রয়েছে। বেইজিং এই সংস্থাগুলির জন্য একটি ব্যাপক সাহায্যের ব্যবস্থা প্রতিষ্ঠা করেছে, যেমনটি মূলত মেড ইন চায়না ২০২৫ কৌশলে বর্ণিত হয়েছে।
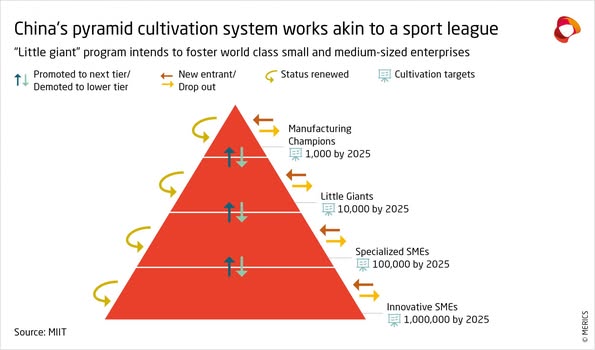
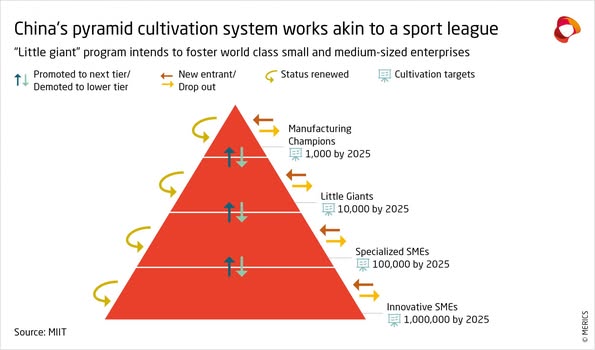
চীনের "এক্সিলারেটর রাষ্ট্র"-এর উত্থান ছোট সংস্থাগুলির প্রতি চীনা নীতিনির্ধারকদের একটি নাটকীয় প্রসারকে চিহ্নিত করে: এটি চারটি ধাপে কাজ করে: প্রথম ধাপে ১ মিলিয়ন উদ্ভাবনী ছোট সংস্থাকে তাদের কাজের ক্ষেত্রের ভিত্তিতে চিহ্নিত করা হয় এবং রাষ্ট্রীয় তহবিল এবং রাষ্ট্রীয় সহায়তা দেওয়া হয়। ১ মিলিয়নের মধ্যে দ্বিতীয় ধাপে, ১00, 000 বিশেষায়িত ছোট সংস্থা নির্বাচিত হয় এবং আরও রাষ্ট্রীয় তহবিল এবং সমর্থন দেওয়া হয়। ১০,০০,০০০ বিশেষায়িতছোট সংস্থাগুলির মধ্যে ১০,০০০ ক্ষুদ্র দানব নির্বাচিত হয় যাদের কেবল আরও বেশি রাষ্ট্রীয় তহবিল এবং সমর্থন দেওয়া হয় না তবে বেসরকারী বিনিয়োগকারী এবং শেয়ার বাজারের সহায়তাও দেওয়া হয়। ১0,000 ক্ষুদ্র দানব থেকে, ১000 উৎপাদন চ্যাম্পিয়নদের তুলে আনা হয়।
পূর্ববর্তী শিল্প নীতি প্রাথমিকভাবে কৌশলগত লক্ষ্য অর্জনের জন্য বৃহত্তর সংস্থাগুলিতে সংস্থানগুলি নির্দেশ করে। কিন্তু এখন ছোট সংস্থাগুলিকে উদ্ভাবনের মূল্যবান উৎস হিসাবে দেখা হয়। এটি কারণ ছোট সংস্থাগুলি সাধারণত লাভের চেয়ে উদ্ভাবনের জন্য স্বতন্ত্র তাগিদ/স্বপ্ন দ্বারা তাড়িত হয়ে কাজ করে। সরকার ক্ষুদ্র দানব এবং অন্যান্য ধরণের উচ্চ-প্রযুক্তির ছোট সংস্থাগুলোকে চয়ন করতে নির্বাচনের মানদণ্ড ব্যবহার করে। পৌরসভা এবং প্রাদেশিক স্তরের কর্মকর্তারা সংস্থাগুলি মূল্যায়ন ও বাছাই করতে সেই উল্লিখিত মানদণ্ডের উপর নির্ভর করে। এরপরে তারা আরও সহায়তার জন্য উচ্চতর কর্তৃপক্ষের কাছে সুপারিশ করে। মানদণ্ডগুলি বিস্তৃত যেমন কুলুঙ্গি পণ্য, বৃদ্ধির কর্মক্ষমতা, আবিষ্কারের পেটেন্ট এবং গবেষণার সংখ্যা। কিন্তু ক্ষুদ্র দানব প্রোগ্রামের প্রথম দুটি ব্যাচে নির্বাচিত ৪৪টি রোবোটিক্স সংস্থাগুলোর একটি নমুনার মধ্যে অনেকেই নির্বাচনের মানদণ্ডগুলো পূরণ করতে ব্যর্থ হয়েছে এবং অপেক্ষাকৃত কম অর্জনকেই মেনে নিতে হয়েছে সরকারের।
বেইজিং বাজার-এর সাথে রাষ্ট্রীয় দিকনির্দেশকে একত্রিত করে: চীন স্থানীয়, প্রাদেশিক এবং জাতীয় পর্যায়ে সক্রিয়, প্রথমে বিশেষায়িত উচ্চ-প্রযুক্তি ছোট সংস্থাগুলিকে সনাক্ত করতে এবং তারপরে তাদের বৃদ্ধি দ্রুত ট্র্যাক করার জন্য একটি গতিশীল মাল্টি-লেভেল মূল্যায়ন এবং সহায়তা সিস্টেম তৈরি করেছে। এর অর্থ সংস্থাগুলিকে মুনাফা বা বিনিময় মূল্যের পরিবর্তে ব্যবহার মূল্য-এর ভিত্তিতে মূল্যায়ন করা হয়। সুতরাং সংস্থাগুলিকে অবশ্যই রাষ্ট্রীয় বিনিয়োগ পেতে প্রযুক্তিগত শর্ত পূরণ করতে হবে। বেশি মুনাফা বিনিয়োগ পাওয়ার মানদণ্ড নয়।
সরকার-প্রত্যয়িত উচ্চ প্রযুক্তির ছোট সংস্থাগুলোকে "বিশেষায়িত ছোট মাঝারি সংস্থা" বা "ক্ষুদ্র দানব" হিসাবে চিহ্নিত করা হয়: তারা প্রত্যক্ষ এবং অপ্রত্যক্ষ রাষ্ট্রীয় সহায়তার একটি বিস্তৃত ব্যবস্থা থেকে উপকৃত হয়। প্রতিযোগিতা ওপর ব্যবস্থাটি প্রতিষ্ঠিত হওয়ায় এই সংস্থাগুলি বিশ্রাম নিতে পারে না এবং তিন বছর পরে সরকারের সহায়তা আবারও অর্জন করতে হয়। সুতরাং সংস্থাগুলি এখন তিন বছর পরে আরও রাষ্ট্রীয় তহবিলের জন্য প্রতিযোগিতা করছে। প্রতিযোগিতা সংস্থাগুলোকে উচ্চতর স্কোর করতে রাষ্ট্রীয় মানদণ্ডের শর্ত অবশ্যই পূরণ করতে হবে। আবারও মুনাফা বিনিয়োগ পাওয়ার জন্য মাপকাঠি নয়।
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General Socialism Communism Xi Jinping Mao USSR China 03-March-2025 by east is risingChinese industrial policy deftly combines state guidance and market mechanisms. By further blurring the lines between state-support and market-forces, Beijing has made it even more difficult for economic partners to assess subsidies of various forms.
Longing after the manufacturing might displayed by Germany’s hidden champions, Chinese policy, think tank and investment banking documents regard them as a model to emulate. The German hidden champions concept has been developed by German management theorist and consultant Hermann Simon to explain the success of German SMEs in global markets. These firms emerged organically from the economic and social circumstances present in Germany, such as excellent vocational training, close ties to social banks, and a distinctive corporate culture. Beijing thinks that it can replicate their success through state intervention, essentially turning a bottom-up process on its head. The very different social and economic environment in China means that it is down to government officials to orchestrate the emergence of local hidden champions. Hence the cultivation system has been set up to identify potential success stories and channel state support.
High-tech small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have emerged as key new players in China’s industrial policy: They have the potential to specialize in niche markets, develop domestic alternatives to foreign inputs and reinforce China’s industrial chain. Beijing has established a comprehensive support system for these firms, as originally outlined in the Made in China 2025 strategy.
The emergence of an “accelerator state” in China marks a dramatic extension of the industrial focus of Chinese policymakers towards smaller companies: It works in four steps: In first step 1 million innovative SMEs are identified on the basis of their area of work and given state funding and state help. In second step among 1 million, 100, 000 specialized EMEs are selected and given more state funds and backing. Among 100,000 specialized EMEs, 10,000 Little Giants are selected who are given not only more state funding and backing but also help from private investors and stock market. From 10,000 Little Giants, 1,000 Manufacturing Champions are endorsed.
Previous industrial policy primarily directed resources to larger firms to achieve strategic goals. Smaller firms are now seen as valuable sources of innovation. This is because smaller firms usually thrives on individual urge/dream to innovate rather than profit. The government uses selection criteria to choose Little Giants and other types of high- tech SMEs. Officials at the municipal and provincial levels rely on them to evaluate and pick companies which they then recommend to higher authorities for further support. The criteria are broad in scope and cover aspects such as niche product focus, growth performance, the number of invention patents and R&D intensity. Out of a sample of 44 robotics firms selected in the first two batches of the Little Giants program, many appear to fall below the selection standards or to undermine its objectives.
Beijing’s tiered-cultivation combines state guidance with market forces: China has developed a dynamic multi-level evaluation and support system, active at the local, provincial and national levels, to first identify specialized high-tech SMEs and then fast-track their growth. This means companies are evaluated on the basis of use-value rather than exchange-value. So companies must fulfill technological conditions to get state investments. Profit is not the criteria for getting more investment.
Government-certified high-tech SMEs are labeled as “Specialized SMEs” or “Little Giants”: They benefit from a comprehensive system of direct and indirect state support. But these firms cannot rest on their laurels as the system is set up to promote competition and after three years the government support has to be earned once again. So the firms are now competing for more state funds after three years. To score high in competition firms must fulfill government given criteria of production. Again profit is not the focus for getting investment.
Officials are channeling ever more finance towards high-tech companies: Beijing has mobilized public financial institutions and is pushing private investors to direct capital towards government-certified start-ups and SMEs, worth tens of billions of yuan. The government has increased loan financing through the banking system and expanded access to equity markets for high-tech SMEs.
The support system seeks to cover all the needs of its SMEs: The government is encouraging all state-connected entities to help high-tech SMEs. This means more state subsidies and R&D support, increased collaboration with universities and research institutes and a more favorable intellectual property system. Officials are also directing large firms to act as financiers, clients and mentors. Big companies are not allowed to buy out successful SMEs. Here again, state is creating hindrances in centralization of production.
The model's Success: The system is channeling more funding to high-tech SMEs. Several state-backed firms such as Leaderdrive and Endovastec in the robotics and MedTech sectors are advancing self-reliance in core technologies.
The Model's Weakness: Yet, there are also signs of weaknesses. The system relies on the capacity of officials to identify the most promising firms, which may be flawed. Support measures could result in significant bad investments and misuse of funds.
The Model's Speciality: Little Giants are increasingly viewed as sound investment options. According to Bloomberg, one venture capital firm only invests in Little Giants.30 Numerous bank reports also highlight Little Giants as aligned with government policy and displaying strong growth potential. So state given certificates are drawing in foreign investments too besides state investments. But private investments show that private players believe the certification processes and evaluation systems.
To be included in the Little Giants program, companies must operate in one of ten priority sectors from the “Made in China 2025” plan. These include computer numerical control (CNC) machining, electric vehicles, or medical devices. Additional evaluation criteria include a company's potential to replace imports or to secure a significant global market share in innovative niche products.
These are government-backed firms which benefit from increased cooperation with large companies, to help them fill supply chain gaps, as well as with universities on research and development (R&D). They are supported in intellectual property rights – and, above all, financially supported. The state acts as a patient investor to early-stage high-tech SMEs by leveraging government guidance funds and through favorable loans from state-owned banks, which serve "Little Giants" in specially created departments.
Companies can also more easily raise capital on the stock markets thanks to simplified listing requirements. In 2022, 40 percent of listings on the Shanghai, Shenzhen and Beijing stock exchanges were made by Little Giants. For example, in September, Hubei Kait Automotive raised CNY 133 million (around EUR 15 million) during its IPO in Beijing. The supplier of automotive electronics and sensors counts Chinese automaker BYD and Volkswagen among its customers.
Numerous Little Giant firms are contributing to China's rise in the e-mobility sector. Guizhou Anda produces battery materials for major battery manufacturers such as CATL, BYD, and CALB. The company was listed on the Beijing stock exchange in March 2023, raising CNY 650 million (around EUR 88 million). Welion, a provider of high-performance solid-state batteries, is rapidly expanding its production capacities and plans to go public by 2025. The company has already won Nio as a customer and has reportedly attracted interest from companies like Volkswagen and Mercedes-Benz.
The Europeans could lose market share in China and globally. The EU’s exports to China are worth EUR 230 billion in total and are heavily concentrated in machinery, vehicles and other manufactured goods. About 40 percent of that could be threatened by Chinese competitors.
Foreign companies producing in China are less vulnerable to China's efforts to secure supply chains. However, domestic competition is growing, especially in sectors that China defines as strategically important, such as mechanical engineering, an area where German companies are especially active.
China's ambitious high-tech SME program ought to be a wake-up call. In many areas, the times when European companies enjoyed a clear technological advantage in China are coming to an end. Europe’s automotive sector, especially in the field of electric vehicles, has already experienced a rude awakening. Now Europe’s Hidden Champions could be next.
[Reference: https://merics.org/en/report/accelerator-state-how-china-fosters-little-giant-companies?fbclid=IwY2xjawIxWVFleHRuA2FlbQIxMAABHWjKwgWyKSeBRK4HT11Xg9wZ0Dd41vta802Fb1wcctwSkYAXm0v8ds7pJw_aem_Frr5mVCBNBcbWJsdk4stUQ ]
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General Socialism Communism Xi Jinping Mao USSR China 02-March-2025 by east is risingChina has edge over US on MUCH MORE than just AI language models
The shock release of a new Chinese AI model known as DeepSeek that’s cheaper, faster and open source sent shockwaves across Silicon Valley, wiping out $1 trln off tech stocks and prompting pundits to dub the new tech a “Sputnik moment” for the US.
But actually, China now dominates the US in 57 of 64 critical technologies, up from just three in 2007, a comprehensive, 20-year 2024 study by the Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI) has calculated.
The US, which led in 60 sectors in 2007, now leads in just seven.
Rankings are based on cumulative innovative and high-impact research and patents.
Where does China excel?
advanced integrated circuit design and fabrication
high-specification machining processes
advanced aircraft engines
drones, swarming and collaborative robots
electric batteries
photovoltaics
advanced radiofrequency communication
Where is US leading?
natural language processing
quantum computing
genetic engineering
China's winning strategy
ASPI credits President Xi Jinping’s ‘Made in China 2025’ plan for the infusion of “massive direct state funding for R&D in key technology,” saying strategic investments already underway were turned into a plan to achieve “technological supremacy.”
Besides research spending, Xi’s strategy has seen “large and complimentary investments…into industrial policy, upgrading supply chains and the manufacturing sector.”
From @SputnikInt
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 02-March-2025 by east is risingBy: Nury Vittachi of Fridayeveryday
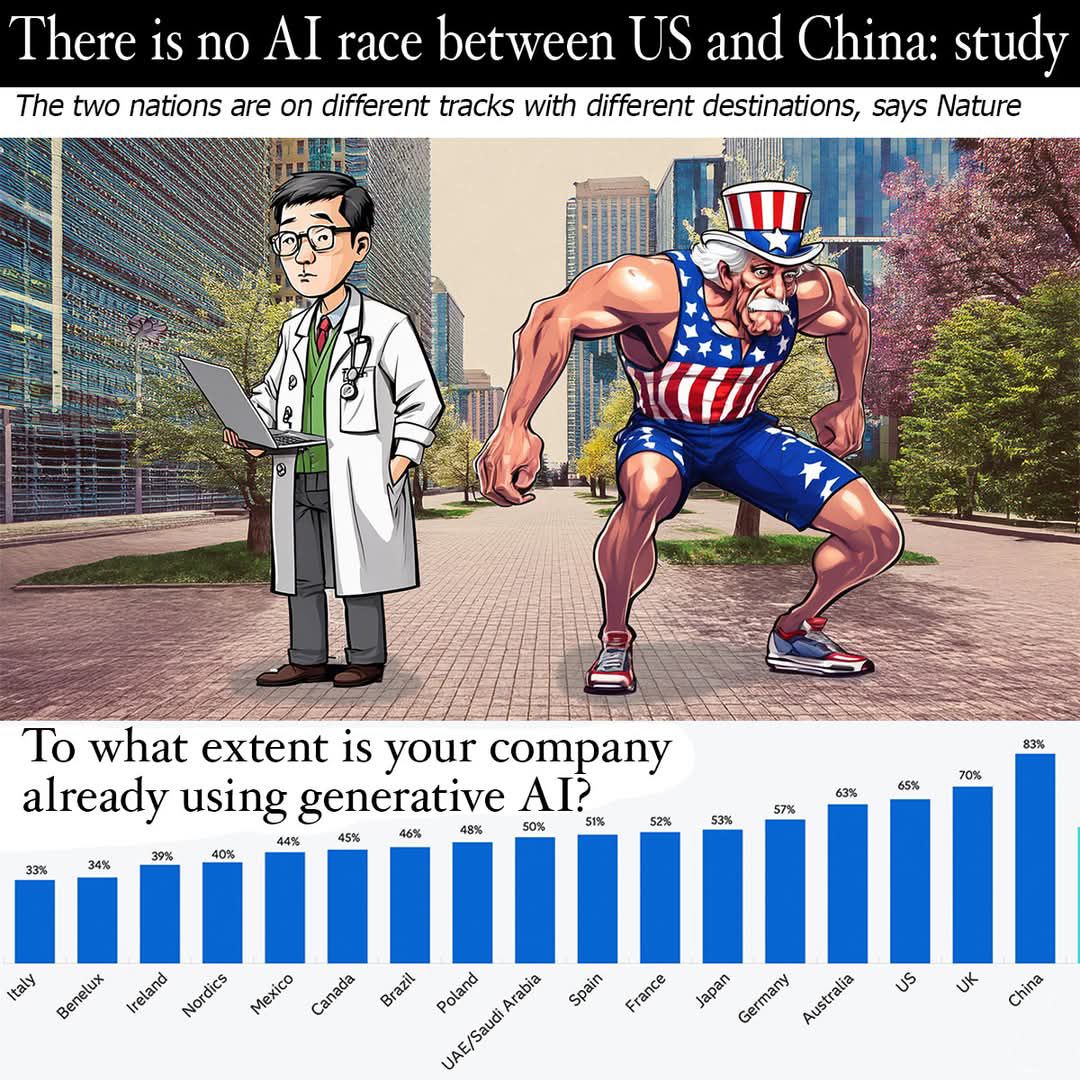
There is no race between China and the US to be top player in AI development, says a new report from Nature, the world's top science journal.
The two countries are on different tracks with different endpoints. The US has been leading the pack in making big, headline-grabbing projects like ChatGPT, while China's focus has been, and remains, the production of practical AI programs that help industrialists, farmers, business people and factories.
AI programs in China are being used "to make trains run on time, monitor fish stocks and provide automated telehealth services," says the report by science writer Jacob Dreyer in the latest edition of the scientific publication.
Ultimately, China will do its usual thing, passing the systems that work to other nations, "especially to lower-income countries," the report says.
DIFFERENT SOURCES OF SUPPORT
In the west, companies need to have innovative ideas that make an impact in the media to attract venture #capitalists to invest. In contrast, China has more of an #engineering school approach—projects must have practical benefit and be shown to be working to get government investment.
"The #divergence in priorities reflects the forces driving innovation in each economy: venture capital in the United States and large-scale manufacturing enterprises and organs of the state in China," Dreyer says.
That doesn't mean that Chinese AI projects are always smaller. One of them is to integrate AI into a system to control the national grid so that the best use can be made of energy.
China is keen to keep its reputation as a leader in making #clean energy options #affordable around the world. "Its emerging AI playbook mirrors its approach to other technologies, such as electric vehicles and clean energy: not the first to innovate, but the first to make them affordable for #widespread use," Dreyer writes.
The huge attention paid to #DeepSeek, a relatively cheap but high performance AI chatbot, has hidden the difference in strategies, inspiring journalists to conjure up the colorful but ultimately inaccurate scenario of a US-China AI "arms race".
STRATEGIC PLAN - FOR FARMERS
The appearance of the Nature report happily coincided with the February 20 publication of a Chinese government "strategic plan" for farmers to use scientific developments, including AI and #genetic modification, to boost crop production and help the country move towards food self-#sufficiency. You can't get much more practical than that.
Other recent data also bolsters the theory that Chinese AI projects may be lower profile, but have already made more inroads in business and industry.
A recent international study of usage of AI revealed that more respondents from China – 83 per cent – said their companies were using AI, than respondents from the United States – at only 65 per cent. In fact, the data in the SAS Generative AI Global Research Report shows that China was ahead of all other nations in the study in this regard (see pic).
[from fridayeveryday. com]
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General USA vs China 25-February-2025 by east is risingThe world is changing whether we yell and scream or not. We don't NEED to have jobs like we have in the past, that's what technology does. But the question is, how can we redesign our society such that we can truly live, steward the earth, and enjoy our time? That is the conversation to be had. JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon offers an optimistic vision of the future, where artificial intelligence could revolutionize work and lifestyle. In a recent interview, he predicted employees might work just 3.5 days weekly and potentially live to 100, driven by technological advancements.
A McKinsey report supports this perspective, suggesting AI could automate 60-70% of current work activities, adding substantial economic value. This aligns with emerging research on shorter workweeks, with one British study showing that reduced work hours can dramatically lower burnout and increase productivity.
That said, we need to see AI as a threat in specific areas. Will it create more multipolar traps? Will we use it for destruction? It is indeed a transformative tool that could fundamentally reshape how we work and live, but it has to be stewarded wisely.
Collective Evolution
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 07-February-2025 by east is rising**"Made in China 2025"** is a strategic plan launched by the Chinese government in 2015 to transform China into a global leader in high-tech industries and advanced manufacturing. The initiative aims to reduce China's reliance on foreign technology, boost domestic innovation, and move the country up the global value chain. Here's a detailed overview of the plan:
---
### **Objectives of Made in China 2025**
1. **Upgrade Manufacturing Capabilities**:
- Shift from low-cost, labor-intensive manufacturing to high-tech, value-added production.
- Focus on innovation, quality, and efficiency.
2. **Reduce Dependence on Foreign Technology**:
- Develop domestic capabilities in key technologies to reduce reliance on imports.
- Achieve self-sufficiency in critical sectors like semiconductors, robotics, and artificial intelligence.
3. **Global Leadership**:
- Position China as a global leader in advanced industries by 2025.
- Compete with developed economies like the United States, Germany, and Japan in high-tech sectors.
---
### **Key Sectors Targeted**
The plan identifies **10 priority sectors** for development:
1. **Information Technology**: Semiconductors, 5G, and AI.
2. **Robotics**: Industrial and service robots.
3. **Aerospace Equipment**: Aircraft, satellites, and space exploration.
4. **Marine Engineering**: Shipbuilding and offshore equipment.
5. **Advanced Rail Transport**: High-speed trains and urban transit systems.
6. **New Energy Vehicles**: Electric and hybrid vehicles.
7. **Power Equipment**: Renewable energy and smart grid technologies.
8. **Agricultural Machinery**: Modern, efficient farming equipment.
9. **New Materials**: Advanced composites and nanomaterials.
10. **Biopharma and Medical Devices**: Cutting-edge healthcare technologies.
---
### **Strategies and Policies**
1. **Government Support**:
- Significant state funding and subsidies for research and development (R&D).
- Tax incentives and low-interest loans for companies in targeted sectors.
2. **Innovation Hubs**:
- Establishment of industrial parks and innovation centers to foster collaboration between academia, industry, and government.
3. **Talent Development**:
- Investment in education and training to build a skilled workforce in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
4. **International Collaboration**:
- Encouraging foreign companies to partner with Chinese firms and transfer technology.
- Acquiring foreign companies and intellectual property to accelerate domestic capabilities.
5. **Standards and Regulations**:
- Developing Chinese technical standards to compete with global standards set by Western countries.
---
### **Progress and Achievements**
Since its launch, **Made in China 2025** has made significant strides:
- China has become a global leader in areas like **5G technology**, **electric vehicles (EVs)**, and **high-speed rail**.
- The country has increased its share of global manufacturing output and R&D spending.
- Chinese companies like **Huawei**, **BYD**, and **DJI** have emerged as global leaders in their respective fields.
However, the initiative has also faced challenges, including:
- **Trade tensions** with the United States and other countries, which view the plan as a threat to their technological dominance.
- **Criticism of unfair practices**, such as forced technology transfer and intellectual property theft.
- **Economic slowdowns** and internal structural issues that have hindered progress in some sectors.
---
### **Global Reactions**
1. **United States**:
- The U.S. has viewed **Made in China 2025** as a strategic threat, leading to trade wars, tariffs, and restrictions on Chinese companies like Huawei and ZTE.
- The U.S. has also increased investment in domestic R&D to counter China's rise.
2. **European Union**:
- The EU has expressed concerns about China's state-led approach and its impact on global competition.
- Some European countries have sought to balance cooperation with China while protecting their own industries.
3. **Developing Countries**:
- Many developing nations see China's advancements as an opportunity for collaboration and investment.
- However, there are concerns about debt dependency and unequal partnerships.
---
### **Future Outlook**
- **Made in China 2025** remains a cornerstone of China's long-term economic strategy, even though the government has downplayed its public emphasis on the plan in recent years due to international backlash.
- The initiative is expected to evolve, with a greater focus on **sustainability**, **green technologies**, and **digital transformation**.
- China's success in achieving its goals will depend on its ability to address internal challenges (e.g., debt, demographic shifts) and navigate geopolitical tensions.
---
In summary, **Made in China 2025** is a bold and ambitious plan that reflects China's aspirations to become a global technological superpower. While it has achieved notable successes, it also faces significant hurdles, both domestically and internationally.
Read MoreAuthor: DeepSeek
Technology news General USA vs China 05-February-2025 by east is risingThe Mars Mission tunnel, a facility built to replicate harsh hypersonic flight conditions, served as the test site. The missile is designed to withstand speeds greater than Mach 9 and is exposed to temperatures reaching 2,192°F (1,200°C). This accomplishment demonstrates China's progress in hypersonic technology, especially in aiming for swiftly moving aerial objects.
Although the missile's exact specifications are yet unknown, the successful testing highlights China's expanding capacity to produce very advanced hypersonic weapons.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
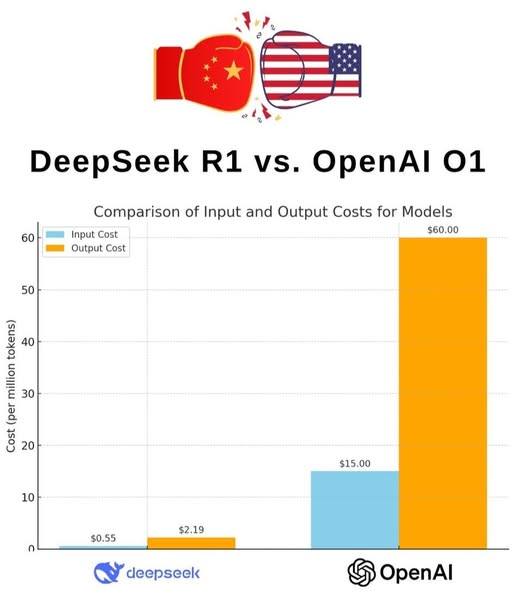
Technology news General USA vs China 27-January-2025 by east is risingIn Financial Capitalism most of the innovative ventures are done for robbing money. In Socialist China, DeepSeek R1 took investment of US $ 0.5 per mn tokens. For producing same Financial Capitalist society's USA's OpenAI O1 took US $ 15.00 per mn tokens. Financial Capitalist USA innovates same thing as Socialist China with 30 times more investment cost. This huge difference shows Financial Capitalist New Industrial Ventures are mostly money laundering through share market by raising share prices. Most of the investment taken through share market are used for fat salaries to CEOs, CFOs, etc. and very meagre amount goes to create the actual product.
This is The Greatest Victory of Socialism over Capitalism. For the 1st time in history, Socialism is proving to finance New Industrial Ventures more efficiently than Financial Capitalism. USSR already proved Socialism's superiority in Socialization of Production in Workplace and China since 1980s have been proving superiority of Socialization of Production in Market as well. Now Socialist superiority in financing New Industrial Ventures is proved as well.
Moreover, even under severe restrictions on AI chip import from USA, DeepSeek R1 beat US companies like OpenAI, Google, MicroSoft, Meta through algorythm optimization. DeepSeek is not only easy to use but also made Open Source which has hollowed out billlions of US Dollar investments by US AI companies.
In the article "Plunder Capital, Merchant Capital, Productive Capital and Speculative Capital" ( https://www.eastisrising.in/view-news/306 ) I wrote: However, when there is free flow of speculative capital, innovative ventures benefit partly because the innovative ventures receive a part of speculative capital investment. However, very little of the loans go to innovative enterprises, and most of them go to shares or stocks of established enterprises or to land, metal, etc.
Now the only positive part of Financial Capital is eclipsed by Socialism.
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General USA vs China 26-January-2025 by east is risingBy Hashem Al-Ghaili
The human Y chromosome, which determines male sex, is slowly disappearing, potentially spelling extinction for humans unless a new sex-determining gene evolves.
But there's hope, as some rodents have already lost their Y chromosomes and found alternative ways to survive.
The Y chromosome contains the SRY gene, which initiates male development in human embryos. However, over millions of years, the Y has been shedding genes. If this trend continues, the last of its remaining 55 genes could vanish in 11 million years.
Rodents like mole voles in Eastern Europe and spiny rats in Japan have lost their Y chromosomes entirely, yet they continue to reproduce. In spiny rats, researchers identified a new sex-determining gene near SOX9 on chromosome 3, which appears to have replaced SRY.
This discovery provides optimism that humans could also evolve a new sex-determining gene. However, this evolutionary process comes with risks. If different sex-determining systems evolve in separate populations, it could lead to reproductive isolation and the emergence of new human species.
In 11 million years, visitors to Earth might find no humans at all — or a world inhabited by multiple human species, each with its own unique way of determining sex.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news Sex War 11-January-2025 by east is risingTaken from Peopl's Daily, China
In 2024, China has achieved yet another series of major breakthroughs in medical science. Let’s look back at some of these most incredible scientific feats! #ThrivingChina
3D-printed SMALLEST micro blood vessel
A China-led international team developed an innovative bioprinting tech — PRINting Cell Embedded Sacrificial Strategy (PRINCESS) — successfully creating a 70-μm endothelialized blood vessel, the tiniest-ever microvasculature, using degradable DNA biolubricant. The tech gives new opportunities for engineering thick tissues, offering the potential to end animal testing.
Pioneer of FIRST treatment for autoimmune disease in ‘Nature’s 10’ list
Xu Huji, a doctor, has been listed by @Nature among the "Ten people who helped shape science in 2024". He led a team of medical professionals in delivering the world's first treatment for autoimmune disease using bioengineered donor-derived CAR-T cells. The treatment's success in three people raises hopes for mass production of cutting-edge CAR-T therapies.
LONGEST-distance remote human surgery
A China-made medical robot has successfully assisted in the longest-distance remote human surgery recently as a surgeon in Shanghai performed a remote prostate cancer surgery for a patient 12,000 km away in Morocco. A doctor took less than two hours to complete the surgery, with a one-way latency of just over 100 milliseconds.
FIRST to cure end-stage type-2 diabetes
For the first time in the world, Chinese doctors successfully treated an end-stage type 2 diabetic patient by implanting islet tissue derived in vitro from his own endoderm stem cells. The patient had been insulin-independent for 33 months as of May 2024.
Read More
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 03-January-2025 by east is risingZahid Mollah
এর কারণ হচ্ছে বিগত ১৫ বছর শেখ হাসিনার মাধ্যমে ভারত বাংলাদেশের সামরিক বাহিনীর মডার্নাইজেশনকে দাবিয়ে রেখেছিল। কিন্তু ৫ই আগস্টের পর নতুন বাংলাদেশের সামরিক বাহিনী দ্রুত বেগে আধুনিকায়নের প্রক্রিয়া শুরু করেছে। হাসিনা ক্ষমতাচুত্য হওয়ার আগেও ও পরে কিছু বিভিন্ন ডিফেন্স পেজ এর সৌর্স সমেত এবং আনুমানিক কানাঘুষার মাধ্যমে মাধ্যমে অর্জিত শপিং লিস্ট দেখা যাক:
Bangladesh Army:
*** Recieved First regiment VT-5 and Rumered to have ordered a second regiment of VT-5 light tank and unknown number of (ARV).
*** Speculative collaboration with Turkiye for MLRS or SRBM.
*** Speculation of Chinese company Vanguard to help build large missile plant in Bangladesh.
*** Bangladesh recieved Huge shipment of Arms and Ammunition from Pakistan shortly after the resignation of Delhi's puppet Hasina.
*** Induction of TRG-230 with 70km range and TRG-300 Kaplan MLRS with a range of 120km, which boosted medium range offensive capabilities.
*** Induction of Independent Army Air Defense Core.
*** Induction of 12 Bayraktar TB-2 and also Army has initiated indegenous UAV program.
*** Induction of Boran 105mm Ultra Light Howitzer from Turkiye.
Air Force:
*** Speculation of 3 squadron of J-10C from China and 12 Rafale Fighter Jet from France. (This might be true even the Air Force chief said they're focusing on MRCA on urgent basis)
*** Operationalized Lalmonirhat Air Base which is within 12km of Chicken Neck
***According to Air Chief, Air Force opting to purchase MRSAM
*** Bangladesh set to sign defence purchase deal with Japan, includes Transfer of Technology (TOT)
*** Bangladesh officially operationalized two high-performance long range radar systems, namely Ground Master 400 (GM400), which have an instrument range exceeding 500km, along with Leonardo RAT-31DL long range air surveillance radar. (which India has objected before because the radar covers huge Indian Airspace)
এইসব মডার্নাইজেশন প্রক্রিয়া বাংলাদেশ আর্মি এবং এয়ার ফোর্সের Qualitative Capability অনেকাংশে বাড়িয়ে দিবে, যেটা ভারতকে চ্যালেঞ্জ ছুড়ে মারে।
বাংলাদেশ সামরিক বাহিনীর সক্ষমতা যদি সত্যিই দুর্বল হতো হাসিনার পতনের পর ভারতীয় সেনাবাহিনী সরাসরি হস্তক্ষেপ না করলেও বর্ডারে অন্তত একটা ক্লাশ করিয়ে চাপ সৃষ্টি করতো। এতোটুকু অসৎসাহস ভারতের আছে।।
কিন্তু সেটাও পারে নাই কারণ সামরিক বাহিনী আগের তুলনায় অনেক বেশি শক্তিশালী
ভারত বাংলাদেশের লং রেঞ্জ অফেন্সিভ ক্যাপাবিলিটিকে ভয় পায়। এদের রিটায়ার্ড (রিটার্ড) জেনারেলদের হাস্যকর পডকাস্ট গুলা দেখলেই বোঝা যায় বাংলাদেশের সামরিক বাহিনী ভারতের জন্য কতটা অস্বস্তিকর।
আর ড. ইউনুসের আমলেই যদি অফেন্সিভ ডিটারেন্স অর্জন করে ফেলে তাহলে ভারতের কফিনে পেরেক মারার মতো হবে। ভারত সম্ভবত তার ইন্টেলিজেন্স সোর্সের মাধ্যমে জানতে পেরেছে ড. ইউনূসের সরকার কিছু দেশের সাথে হয়তো স্ট্র্যাটেজিক চুক্তি করতে পারে।
সেনাপ্রধান গতকাল তার বক্তব্যে সশস্ত্র বাহিনীকে আধুনিক সরঞ্জাম দিয়ে আধুনিকায়নের কথা ব্যক্ত করেছে। আশা করা যায় বাংলাদেশের সামরিক শক্তি একটা বুস্ট নিবে।
INDIA is passing through GD Bakhsi Phenomena
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news Hindu 06-December-2024 by east is risingFrom Facebook post of Fred BeGood
China has successfully tested a groundbreaking nuclear reactor that eliminates the risk of meltdown, a major leap forward in nuclear safety.
Located at the Shidao Bay Nuclear Plant, the HTR-PM reactor uses a pebble bed design with TRISO fuel—tiny, ceramic-coated uranium particles designed to contain fission products even under extreme temperatures.
Unlike traditional reactors that rely on water cooling, the HTR-PM can naturally dissipate heat through conduction, radiation, and convection, allowing it to remain stable without power.
In two full-scale tests conducted in 2023, the reactor demonstrated its ability to safely shut down and dissipate heat during complete power loss. Temperatures peaked at just 870°C, far below the catastrophic levels seen in disasters like Fukushima, where temperatures soared to 2800°C.
The HTR-PM’s self-cooling capability ensures it can avoid the kind of catastrophic failures that have historically undermined public trust in nuclear energy.
This innovation is part of a larger global push for safer, more sustainable nuclear power. The reactor generates 200 MW, positioning it as a promising alternative for clean energy. Its success could pave the way for broader adoption of advanced reactor designs, providing a critical boost for nuclear energy during the transition to a greener future.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 06-December-2024 by east is risingIndustry experts predict a bright future for China’s EV industry, with the potential to capture a staggering 60% of the global market share by 2030. This translates to a projected annual sales volume of 60 million EVs, a significant jump from the current global figure. This optimistic outlook stems from a confluence of factors. Firstly, China already boasts a commanding 32% share of the global automobile market and over 60% of the global EV market share.
Secondly, the shift towards EVs presents a unique opportunity for China to “overtake on a curve.” While traditional automakers from Europe, America, and Japan previously dominated the market with their expertise in internal combustion engine technology, the rise of EVs has leveled the playing field. Batteries, motors, and electronic controls – the core components of EVs – are areas where China has rapidly developed its capabilities. China’s success in the EV market can be attributed to government incentives like subsidies and infrastructure, a vast domestic market with a growing middle class, and a surge in homegrown EV technology that challenges established players. This potent mix has propelled China to the top of the global EV market.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 02-July-2024 by east is risingLearn all about China's advanced satellite navigation system that is surpassing America's in 2024. Discover the technology behind China's INSANE satellite system and how it is outperforming the competition. Find out the reasons behind China's success in satellite navigation and why it is a game-changer in the global space race. Stay tuned to understand the implications of China's dominance in satellite technology. There are several noteworthy aspects of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System that have sparked curiosity and indicate a growing competitive edge: 1. Global Coverage 2. Accuracy and Signal Integrity 3. Technology and Innovation 4. Market Penetration and Partnerships 5. Integration and Compatibility It's surprising because, traditionally, GPS has been seen as the gold standard in satellite navigation, with a first-mover advantage and widespread global adoption. China's rapid progress with BeiDou challenges this perception and highlights the competitive nature of global satellite navigation systems. The United States faces several challenges in competing with China's advanced satellite navigation technology, represented by BeiDou. These challenges span technological, strategic, economic, and geopolitical dimensions. 1. Technological and Standards Challenges 2. Economic and Market Challenges 3. Cost and Accessibility 4. Strategic and Geopolitical Challenges 5. Space Debris and Environmental Concerns 6. International Challenges China's BeiDou has made significant advancements that, in certain aspects, surpass or complement American GPS technology. Here are some of the key areas where BeiDou has made strides: 1. Global Coverage 2. Precision and Reliability 3. Anti-jamming Capabilities 4. Short Message Communication 5. Interoperability and Compatibility 6. Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) 7. Integration with Other Technologies 8. Launch Frequency and Expansion 9. Geopolitical and Economic Leverage China's BeiDou has emerged as a dominant player in the field of satellite navigation technology, challenging the long-standing supremacy of the American GPS system. Key aspects of China's dominance include: 1. Technical Advancements: BeiDou has achieved parity with GPS in terms of accuracy and coverage, with plans to surpass it in certain areas. The system's third generation promises even greater capabilities. 2. Global Expansion: BeiDou has expanded its coverage to nearly every region of the world, with a global network of satellites providing reliable services. This global presence is a significant milestone in China's space ambitions. 3. Integration with Other Technologies: BeiDou is being integrated with 5G networks and the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling a wide range of applications from smart cities to autonomous vehicles, enhancing its utility and competitiveness. 4. Rapid Expansion and Launch Frequency: China's capability in launching satellites at a rapid pace has enabled the swift expansion of BeiDou, allowing for quick adaptation to new requirements and market demands. 5. Geopolitical and Economic Leverage: Offering an alternative to GPS, BeiDou provides China with geopolitical and economic leverage, expanding its influence through international partnerships and agreements. 6. Disaster Response and Relief: During the 2015 Nepal earthquake, BeiDou demonstrated its superiority in emergency response situations, showcasing its unique strengths in real-world applications where traditional navigation systems might face limitations. China's BeiDou has not only matched the capabilities of GPS but has also begun to demonstrate its own unique advantages, particularly in areas such as user-to-user communication and integration with other technologies. This has positioned BeiDou as a significant player in the global navigation satellite system market, challenging the traditional dominance of GPS and highlighting China's leadership in satellite navigation technology. Please share your thoughts about Beidou and subscribe for more updates about the China’s latest satellite technology development. That’s all we have for now, and thank you for tuning in.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General USA vs China 23-June-2024 by east is risingThe groundbreaking claim made by a Chinese team of researchers regarding the new ferroelectric storage chip revolves around its near-infinite lifespan. This innovative technology is reported to have the potential for an essentially limitless lifespan, significantly surpassing the endurance of existing storage devices. In this video, we will dissect the specification of this storage chip and why this breakthrough has a profound impact on China’s quest in becoming the leader in advanced technology. Ferroelectric materials can store data without power, making them promising for non-volatile memory applications. The Chinese team's development involves a novel ferroelectric material and architecture that they claim can endure an unprecedented number of write-erase cycles. Traditional flash memory, for comparison, has a limited lifespan measured in thousands to tens of thousands of write-erase cycles. The claim of near-infinite lifespan is based on the unique properties of the ferroelectric material used, which does not suffer from the physical wearout that limits the life of traditional non-volatile memory. This could revolutionize data storage, offering devices that retain their storage capacity and performance over extremely long periods without degradation. The Chinese team's development of a ferroelectric storage chip with a near-infinite lifespan represents a significant breakthrough in the field of storage technology. The key findings and breakthroughs that make this chip revolutionary include: 1. Extended Lifespan 2. Low Power Consumption 3. High Endurance 4. Fast Read and Write Speeds 5. Resilience to Environmental Factors 6. Data Retention 7. Scalability 8. Cost-Effectiveness The development of a ferroelectric storage chip with a near-infinite lifespan represents a groundbreaking advancement in storage technology. The key breakthroughs include its extended lifespan, low power consumption, high endurance, fast read and write speeds, resilience to environmental factors, data retention capabilities, scalability, and potential cost-effectiveness. These features make the ferroelectric storage chip particularly attractive for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to data centers and long-term archival storage. The potential impact of this technology is significant, as it could lead to more energy-efficient, durable, and high-performance storage solutions, ultimately transforming the landscape of data storage and management. We will follow up on this amazing advancements in storage technology and report back when we hear more in the future. That’s all we have for now, and thank you for tuning in.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 23-June-2024 by east is risingConcerns that cheap Chinese semiconductors will flood the market may be premature
hina’s hunger for homemade chips is insatiable. In May it was revealed that the government had launched the third iteration of its “Big Fund”, an investment vehicle designed to shore up the domestic semiconductor industry. The $48bn cash infusion is aimed at expanding the manufacture of microprocessors. Its generosity roughly matches similar packages from America ($53bn) and the eu ($49bn), both of which are also trying to encourage the expansion of local chipmaking.
Chinese chipmakers are in a tough spot. In October 2022 America’s government restricted the export to China of advanced chips and chipmaking gear made using American intellectual property—which is to say virtually all such devices. This makes it near-impossible for Chinese firms to produce leading-edge microprocessors, the kind whose transistors measure a few nanometres (billionths of a metre) across and which power the latest artificial-intelligence models. But it does not stop them cranking out less advanced chips, with transistor sizes measured in tens of nanometres, of the sort that are needed in everything from televisions and thermostats to refrigerators and cars.
Chips off the old block
As a consequence, semiconductor companies from China increasingly dominate chipmaking’s lagging edge. They account for more than half of all planned expansion in global manufacturing capacity for mature chips. TrendForce, a research firm, forecasts that China’s share of total capacity will increase from 31% in 2023 to 39% in 2027.
This has alarmed Western policymakers. In April Gina Raimondo, America’s commerce secretary, warned that China’s “massive subsidisation” of their manufacture could lead to a “huge market distortion”. America and the eu have launched reviews to gauge the effect of China’s legacy-chip build-up on critical infrastructure and supply-chain security. Bosses of Western chip firms privately grumble that the coming glut of Chinese semiconductors will put downward pressure on prices both in China, from which foreign chipmakers derive large portions of their revenues, and elsewhere. Even some of their Chinese counterparts agree. They include smic, China’s biggest foundry (as contract manufacturers that make chips based on their customers’ blueprint are known). Last month it warned investors that competition in the industry “has been increasingly fierce” and that it expected prices to fall.
Chinese investments certainly suggest ambitious plans. In 2022 China imported chipmaking equipment worth $22bn. The following year it bought $32bn-worth of similar tools, accounting for a third of worldwide sales. Customs data show that in the first four months of 2024 Chinese imports of chipmaking tools were nearly double those in the same period last year (see chart 2). Since American export controls bar the most sophisticated equipment from reaching China, the bulk of those imports are likely to consist of kit used to make lagging-edge chips, not leading-edge ones. Chinese chipmakers have also been buying more equipment from Chinese toolmakers, whose market share at home has risen from 4% in 2019 to an estimated 14%. Because homemade equipment is years behind the technological cutting edge, it is likewise destined for the production of mature chips.
Listen to this story. Enjoy more audio and podcasts on iOS or Android.
China’s hunger for homemade chips is insatiable. In May it was revealed that the government had launched the third iteration of its “Big Fund”, an investment vehicle designed to shore up the domestic semiconductor industry. The $48bn cash infusion is aimed at expanding the manufacture of microprocessors. Its generosity roughly matches similar packages from America ($53bn) and the eu ($49bn), both of which are also trying to encourage the expansion of local chipmaking.
Chinese chipmakers are in a tough spot. In October 2022 America’s government restricted the export to China of advanced chips and chipmaking gear made using American intellectual property—which is to say virtually all such devices. This makes it near-impossible for Chinese firms to produce leading-edge microprocessors, the kind whose transistors measure a few nanometres (billionths of a metre) across and which power the latest artificial-intelligence models. But it does not stop them cranking out less advanced chips, with transistor sizes measured in tens of nanometres, of the sort that are needed in everything from televisions and thermostats to refrigerators and cars.
Chips off the old block
As a consequence, semiconductor companies from China increasingly dominate chipmaking’s lagging edge. They account for more than half of all planned expansion in global manufacturing capacity for mature chips. TrendForce, a research firm, forecasts that China’s share of total capacity will increase from 31% in 2023 to 39% in 2027 (see chart 1).
chart: the economist
This has alarmed Western policymakers. In April Gina Raimondo, America’s commerce secretary, warned that China’s “massive subsidisation” of their manufacture could lead to a “huge market distortion”. America and the eu have launched reviews to gauge the effect of China’s legacy-chip build-up on critical infrastructure and supply-chain security. Bosses of Western chip firms privately grumble that the coming glut of Chinese semiconductors will put downward pressure on prices both in China, from which foreign chipmakers derive large portions of their revenues, and elsewhere. Even some of their Chinese counterparts agree. They include smic, China’s biggest foundry (as contract manufacturers that make chips based on their customers’ blueprint are known). Last month it warned investors that competition in the industry “has been increasingly fierce” and that it expected prices to fall.
chart: the economist
Chinese investments certainly suggest ambitious plans. In 2022 China imported chipmaking equipment worth $22bn. The following year it bought $32bn-worth of similar tools, accounting for a third of worldwide sales. Customs data show that in the first four months of 2024 Chinese imports of chipmaking tools were nearly double those in the same period last year (see chart 2). Since American export controls bar the most sophisticated equipment from reaching China, the bulk of those imports are likely to consist of kit used to make lagging-edge chips, not leading-edge ones. Chinese chipmakers have also been buying more equipment from Chinese toolmakers, whose market share at home has risen from 4% in 2019 to an estimated 14%. Because homemade equipment is years behind the technological cutting edge, it is likewise destined for the production of mature chips.
Still, fears that this threatens the security of the West’s supply chains may be misplaced. Jan-Peter Kleinhans of snv, a German think-tank, reckons most of the new production will be “in China, for China”. In 2018 smic and Hua Hong Semiconductor, another foundry, generated nearly 40% of their revenue from foreign customers. This fell to 20% last year. At the same time Chinese foundries’ overall output increased, reflecting robust domestic demand.
This demand looks likely to remain strong. Bernstein, a broker, estimates that Chinese carmakers, electronics firms and other chip users buy almost a quarter of the world’s mature semiconductors. Almost half of those purchases still come from abroad whereas they could be coming from home.
There is another reason for the West to keep its cool. Although Chinese chipmakers rival foreign makers of mature semiconductors in manufacturing, they are still outmatched when it comes to design, engineering and product reliability. This is especially true for fiddly semiconductors such as microcontrollers (a type of computer-on-a-chip) and analogue processors (which use wave-like signals instead of digital ones and zeros). Having doubled their domestic market share to around 12% between 2019 and 2021, Chinese makers of analogue chips have been unable to make further inroads since. Bernstein expects them to supply just 14% of the domestic market by 2026. That leaves lots of room for Western producers such as Analog Devices, Texas Instruments and nxp.
More surprisingly, Chinese foundries are also at a cost disadvantage. In contrast to leading-edge chip factories, which must upgrade their expensive equipment frequently as transistors shrink, most mature-chip manufacturers operate the same equipment for a long time. So long, in fact, that established companies have fully depreciated the value of many of their assets. This significantly lowers their unit costs, a boon at a time when competition keeps prices down. Chinese chipmakers which are investing in new capacity right now will have to absorb the hefty cost of those investments for several years. That means considerably thinner margins and therefore less money to reinvest in future growth. If China’s government wants that growth to continue, the third Big Fund will not be the last.
Taken From Economist
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General USA vs China 09-June-2024 by east is risingPreviously, Chinese cars received low ratings in crash tests and aroused skepticism among Russian motorists.
However, today many models receive high ratings in the EuroNCAP and C-NCAP crash tests.
For example, Voyah Free and Geely Monjaro received the maximum five stars, and Nio ET5 became the safest car of 2023 according to EuroNCAP.
Improvements are associated with the use of advanced technologies and high-strength materials in the body structure. For example, the basic Changan CS35 Plus has 2 airbags, active head restraints and ABS and EBD systems. Older models have 6 pillows.
In the Changan Uni-V, the Forward Collision Warning (FCW) system can initiate emergency braking. Geely and Belgee use Volvo's blind spot monitoring system. Older Changan models have a safe exit system that warns of approaching traffic when the door is opened. The flagship Geely Monjaro has a CMSF collision avoidance assistant.
@zr_ru on Telegram
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
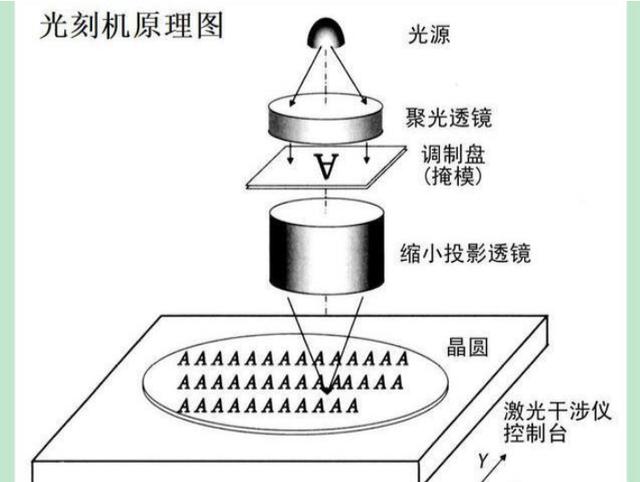
Technology news General 27-May-2024 by east is risingThe sophistication of EUV relates mainly to a wavelength measuring just 13.5 nanometers, considerably less than the 193 nanometers of deep ultraviolet (DUV) lithography, an older technology previously shipped to China in large volumes. The difference, an ASML spokesperson once told Light Reading, is like that between a thick marker and a fine ballpoint.
This analogy suggested that using DUV machines to produce complex 7-nanometer chips would be like drawing an intricate portrait with a fat pen. But SMIC is believed to have done it via a technique called multiple patterning. As the name implies, this essentially means repeating the lithographic process with DUV equipment to achieve the desired results. Double- and quadruple-patterning are among the specific options available.
The main uncertainty is at what cost, and some evidence of multiple patterning's economic disadvantages may have emerged in SMIC's results. In the latest, published a few days ago, SMIC reported a 20% year-over-year increase in first-quarter sales, to about $1.75 billion, and yet profits tumbled 73%, to $63.5 million. Executives at the company laid most of the blame on high depreciation charges, incurred as new equipment was powered up for the first time.
But an examination of SMIC's results also reveals a 31% rise in cost of sales, to more than $1.5 billion. SMIC's gross margin accordingly sank from about 21% a year ago to less than 14%. Richard Windsor, an analyst with Radio Free Mobile, thinks the workaround of using DUV and multiple patterning to make those 7-nanometer chips has proven expensive.
Experts say the big drawback of multiple patterning is that it tends to result in lower "yields," a percentage measure of the functional chips derived from a silicon wafer. Intel is thought to have experimented with it for 10-nanometer production before it eventually gave up and bought EUV machines instead. TSMC had a similar experience, according to Windsor. In a blog, he writes that yields were so low as to be uneconomical.
"However, we are expected to believe that SMIC has got this to work well enough so that its yields are economic and that it is making money," he said. "I think that the reverse is true and that a part of the weakness we have seen in gross margins over the last several quarters is due to increasing revenues coming from chips made using multi-patterning techniques."
There was certainly no acknowledgement of this in SMIC's first-quarter report or commentary prepared by executives for their earnings call with analysts. But Windsor is not the only expert questioning those cost-of-sales numbers. Earl Lum, the founder of EJL Wireless Research, who previously worked in the chip industry, agrees that a 31% increase may be a sign of "a potential yield hit."
US hawks will celebrate anything that points to problems for Chinese technology companies, especially those involved in chips. If Windsor and others are right, then growing shipments of Huawei's newest phones may chew further into SMIC's profits and potentially hurt its competitiveness. The alternative could be higher prices for end users, making rivals based outside China seem a much better bet.
SMIC's options, though, are limited. Japan's Canon and Nikon are the only other big makers of lithography machines. Regardless of Japan's appetite for upholding sanctions against China, neither company has an EUV range of products. Developing that expertise took many years, cost billions and necessitated partnerships with chip companies and component makers worldwide, ASML insists. China is reportedly aiming for self-sufficiency in EUV, among other things, and it is not shy of long-term commitments. But a homegrown Chinese rival could be a long time in the making.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General USA vs China 26-May-2024 by east is risingThe Uyghurs played a significant role along the Ancient Silk Road, particularly in the region of Xinjiang, which was a crucial crossroads on the trade routes. Here's how the Uyghurs fit into the context of the Silk Road:
1. Uyghur Civilization: The Uyghurs are a Turkic ethnic group with a rich cultural heritage. They have historically inhabited the region of Xinjiang in present-day China, which was a critical juncture along the northern branch of the Silk Road.
2. Trade and Interaction: The Uyghur civilization flourished along the Silk Road route in the oasis cities. Cities such as Kashgar, Turpan, and Khotan were important trading hubs where goods and ideas from East and West converged. Uyghurs engaged in trade, craftsmanship, and cultural exchange with merchants and travellers from various backgrounds.
3. Cultural Fusion: Due to their location at the crossroads of different civilizations, the Uyghurs experienced a blending of cultures. This is reflected in their language, which is Turkic, with significant influences from Persian, Arabic, and Chinese. Art, architecture, cuisine, and music also reflect this cultural fusion.
4. Religion and Beliefs: Along with trade, the Silk Road facilitated the spread of religions. The Uyghurs practised various faiths, including Buddhism, Manichaeism, Nestorian Christianity, and later Islam. This diversity contributed to the region's cultural vibrancy.
5. Oasis Cities: The Uyghur-inhabited oasis cities were crucial for travellers and traders as rest stops, providing essential services such as food, water, shelter, and markets for goods. These cities were innovation centres in agriculture, irrigation, and urban planning.
6. Decline and Revival: Like the Silk Road, Uyghur culture and heritage faced challenges over time, including political changes and shifts in trade routes. In modern times, the Uyghurs have faced issues related to cultural preservation, human rights, and political tensions in the Xinjiang region.
7. Cultural Heritage: Despite challenges, efforts are ongoing to preserve and promote Uyghur culture, language, and traditions. This includes initiatives to protect historical sites, promote Uyghur arts and crafts, and raise awareness about the Uyghur people's contributions to Silk Road history.
Including the Uyghur perspective enriches the narrative of the Silk Road, highlighting the diverse peoples and cultures that contributed to its vibrant history.
(Copied from Uyghur Bookshelf)
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 08-April-2024 by east is risingBecause a technology is created after spending millions of money and years of time.
But whether that technology can be commercially employable is unknown to the technology creators.
For commercial viability a technology needs to be employed in a big market with high population and high purchasing power. Only then there is maximum chance that the technology can be employable & invested money will return & may be with profit.
European companies have small domestic economy with high purchasing power but low population.
So the best option for them is to sell their technologies to USA and now to China and earn a good profit covering the cost.
USSR also had same problem with USA since 1974 Nixon Breznev Deal. USSR was highest patent holder and creator of latest technologies. But USSR had to sell their technologies to USA which had three times higher purchasing power. That was an important reason why Socialist Block failed to gain handsomely from opening up of Breznev Era. This was well observed in Perestroika by Gorbachev.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 08-April-2024 by east is risingJapan and the Netherlands agreed with the U.S. to restrict exports of advanced chip-manufacturing equipment to China. How will it hurt China's chip industry?
Hands off China , let’s first see How the U.S. suppressed Japan's chip industry
China has not the only country targeted by the U.S. in the semiconductor sector.
In the 1980s, Japan, one of the U.S.'s closest allies, once produced about half of the world's semiconductors. In the year 1990, six of the world's top ten semiconductor manufacturers were Japanese companies.
In order to contain Japan's semiconductor industry, the U.S. launched the "301" investigation, threatened to label Japan as conducting unfair trade, and imposed retaliatory tariffs, forcing Japan to sign the U.S.-Japan Semiconductor Agreement.
As a result, Japanese semiconductor enterprises were almost completely driven out of global competition, and their market share dropped from 50 percent to 10 percent.
In the same time, with the support of the U.S. government, a large number of U.S. semiconductor enterprises took the opportunity and grabbed larger market share.
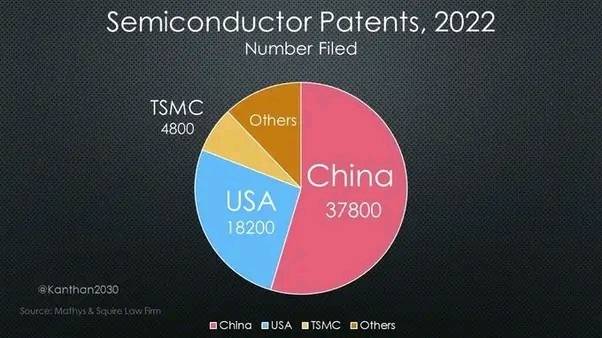
But China does have a different opponent, one that the United States has probably never encountered in its less than three hundred years of history. Take a quick look at the data for 2022
US tries to slow Chinas growth by denying China access to chip technology. But 55% of the semiconductor patents in the world came from China last year. That's more than twice as much as the US.
Are the Americans certain this is a war they will win?
(collected from Facebook)
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 08-April-2024 by east is risingJoshua Biswas Analysis:
I often hear some Indians say that India will be able to inflict massive damage on China during a war because India has a huge population of expendable young men amongst its citizens and entire citizenry will take up arms. I think that is completely false assumption and here is why
1. During any war with China, China will have the ability to take out ammunition depots and arms factories deep inside enemy line using its rocket force, satellites and drones for kinetic strikes. It will also have the cyber capability to insert stuxnet like viruses into the CNC machines and other tools of the factories to make their motors run out of control and lead to a sabotage or CATO. So how will you arm you citizens?
2. China will be able to take out India's power grid using cyber attacks and rocket and drones. When it goes dark your citizens will be busy looting and doing other s*xual crimes
3. Take out the railway networks using the same as above and also take help of maoist rebels inside India. Without train how will you transport them to front?
4. India won't be able to create decentralized arms industry to keep up with small arms and ammo production because India doesn't have that sort of skills since India is not a gun culture like Pakistan is, where people from Peshawar can build guns (including AKs and LMGs) and ammo in their small workshops and keep their fighters supplied even when their land gets invaded. Without a gun culture your citizens will not be able to arm or train themselves !
5. Most Indian civilians from majority community are religiously motivated and stick together due to islamophobia, but China is not a Muslim nation so why will they unite against it???
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 20-March-2024 by east is risingIndia's Chandrayaan-3 on Wednesday became the first spacecraft to land in the lunar south pole region, making India the fourth nation to successfully land a spacecraft on the moon. India's historic landing near the Moon's unexplored south pole has won it wide congratulations across the world.
Landing on the moon's rugged south pole is full of challenges. A previous Indian bid failed in 2019 and Russia's Luna-25 failed in a similar mission less than a week ago. The soft landing of India's Chandrayaan-3 also came after nearly a month of frequent and complicated adjustment.
In addition to bringing scientific value to space exploration, Chandrayaan-3 also carries the "space ambition" of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi. Developing the space sector is a key plank of Modi's "Make in India" campaign, which aims to position India as an important hub for technological innovation. His administration hopes that breakthroughs in space missions can promote growth of India's manufacturing sector and the wider economy.
To realize the goal of being a frontrunner in the space arena, the Modi government in 2020 began to encourage private space launches and investment in satellite businesses.
India this year also introduced the Indian Space Policy 2023, detailing plans to boost space economy opportunities. The Modi government plans to increase India's share of the global private space launch market from 2 percent in 2020 to 10 percent over the next decade.
Chandrayaan-3 is regarded as the first major mission since the implementation of this series of policies. Its successful landing on the moon has undoubtedly boosted India's confidence in its ambition to earn a bigger share of the vast space economy.
However, the realization of India's moon landing dream, which was also full of twists and turns, does not mean it is ready to provide opportunities to India's manufacturing and overall economy. India must face the fact that there is still a long way to go.
A Bloomberg article in April titled "India is taking on China in the $447 billion space economy" said that India is muscling in on the increasingly lucrative space sector, taking advantage of the West's geopolitical isolation of China and Russia to pitch itself as a major provider of satellite launches.
Indeed, from the perspective of geopolitics, the development of India's space sector has advantages compared with China and Russia. However, India still has far to go before it can catch China. As of March 2020, China owned 13.6 percent of all earth-orbiting satellites, compared to 2.3 percent for India, according to media reporting, citing a US think tank.
While China conducted 64 launches in 2022, India managed five similar launches. In the past, India's rockets have also suffered from reliability issues. Its success rate in recent years was just about 70 percent, lower than the success rates of rockets from the US, Europe, Russia or China, according to Jonathan McDowell, an astrophysicist at the Center for Astrophysics, which is operated by Harvard University and the Smithsonian Institution, the Bloomberg said.
This time, Chandrayaan-3 has accomplished the soft landing on the moon, but some deficiencies have also been exposed during the mission, including insufficient carrying capacity, insufficient orbital accuracy, and insufficient orbit determination capabilities.
Admittedly, India has cost advantages and geopolitical advantages in commercial aerospace and broader manufacturing, but it will not be easy to turn them into a driving force for industrial and economic growth. India still faces many difficulties in seeking a bigger market share in the commercial aerospace market and high-tech manufacturing, so more extensive efforts are needed.
The author is a reporter with the Global Times
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 26-August-2023 by east is risinglndians think they have landed on Moon while Russians have failed.
They don't know Rus is working on new tech, while lnd is copying 1960s Soviet tech.
Successful to Failure data
Soviet : 18/38
USA : 37/15
China : 4/0
India : 1/2
Soviet has failed most and this is because Soviet used new technology most times and hence succeeded after constant failures. Now post 1991 Russia is working on raising the speed of Moon landing.
USA succeeded more as it used same proven technologies most times. It helped USA to make all old technologies perfect. US having more resources than Russia was able to do it.
For China other than landing on dark side of the Moon other three can't be called new tech. Surely making use of a new tech perfectly at the first chance is a great job. Only China can match the resource of USA and that is the reason China is only competitor of USA in space tech.
Why soft landing on Dark side of the Moon is so important?
1. Since the dark side of moon never faces earth, hence the earth borne communication systems like antenna will have no direct line of sight with the craft during descend, that means Chinese must have used some form of advanced A.I system to guide the craft to the pitch black dark grounds of moon, because without a direct line of sight from earth a manual control from earth is not going to be reliable. Hence Chinese A.I excelled here. In other word the Chinese craft was flying autonomously
2. Chinese have used sophisticated optical, electro optical and night vision equipment for the dark side operation, duh ! Superior to anything anyone used in past on lunar surface
India has succeeded in adapting 1960s Soviet technology of Moon landing in 2023 and that also after failing two times. India has landed closest to South Pole and that actually has no technological significance.
UAE-Japan may be next to land on Moon together which will be 1990s technology.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 25-August-2023 by east is risingChip less than 7 nm is important in the global semi conductor market but it is not the decisive factor. Market share of less than 7 nm chip is very small now. 2021 Report of China Semi conductor Industry Association states that market share of below 7 nm chip in the global market is mere 2% at the moment. But market share of 14 nm and above 14 nm chips is 70%. Moreover, TSMC Quarter 1, Report states that 14 nm and above 14 nm chips account for 60% of revenue globally.
Downstream market for below 7 nm chips is shrinking while it is expanding rapidly for 14 nm and above 14 nm chips. Below 7 nm chips are mainly needed to make smart-phones and global market for smart-phones has little room to expand. In fact, global smart-phone shipments are shrinking for four consecutive years. But 14 nm and above 14 nm chips are mainly required in Electric Vehicles, new 5G-AI-IoT related machines and robots. So demand for 14 nm and above 14 nm chips is rising and likely to rise further in the age of Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship linked to gains from experience in production. In 1975, looking forward to the next decade, he revised the forecast to doubling every two years, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41%. Moore's prediction has been used in the semiconductor industry to guide long-term planning and to set targets for research and development, thus functioning to some extent as a self-fulfilling prophecy.
Moore in 2016 said that Moore's Law is no longer working. This is because since TSMC broke through the production of 14 nm chips, time consumed for each new lower nm chip production is often several times than that of the production of previous high nm chip production. It is predicted that 1 nm is going to be the limit below which no silicon chip making will be possible. It is already possible to make 3 nm chips commercially and 2 nm chips in research level. So further improvement of silicon chips will be even more difficult.
These three points clearly prove that US chip war on China has little chance to succeed. Firstly, China can already produce 14 nm and above 14 nm chips at mass level and hence will continue to share 60% of the global revenue from chip production. With this revenue China can easily carry on its research to produce less than 7 nm chips independently. But USA will have to content by monopolizing mere less than 2% of the global chip market as US companies have already been asked to avoid Chinese buyers. USA will find it more difficult to reduce the size of chips while China will find it relatively easier to catch up.
The only way to size down the chips further is by moving from silicon chips to photonic chips or graphine (carbon) chips. Chinese research is ahead of US in both photonic chips and graphine chips. So US has little prospect of using its power of being historically ahead in these two fields unlike the case of silicon chips.
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General USA vs China 12-March-2023 by east is risingU.S. and China has entered new space race with Artemis lunar rocket launch.
China has successfully sent a new team of astronauts to its Tiangong space station. This is a significant achievement that not only marks the country’s first in-orbit crew handover but possibly also the beginning of continuous occupancy at the station.
The rendezvous in space marks a milestone for China’s rapidly advancing space program as Beijing aims to catch up with and eventually surpass the United States as the dominant power in space.
The three-man crew arrived at the space station Wednesday aboard a Shenzhou-15 spacecraft to take over from three colleagues who had arrived in June and are set to return next week.
The new team will stay for six months and focus on installing equipment around the newly completed, three-module station, which will host a variety of experiments in near-zero gravity and become only the second permanently inhabited space outpost after the NASA-led International Space Station.
The Tiangong station is set to operate for about a decade in low-Earth orbit, while the ISS is expected to conclude operations by 2030.
Tiangong Chinese: 天宮 Tiāngōng; lit. 'Palace in the Sky'officially the Tiangong space station (Chinese: 天宫空间站; pinyin: Tiāngōng kōngjiānzhàn), is a space station constructed by China and operated by China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) in low Earth orbit between 340 and 450 km (210 and 280 mi) above the surface. Being China's first long-term space station and the core of the "Third Step" of the China Manned Space Program, it has a mass between 90 and 100 t (200,000 and 220,000 lb), roughly one-fifth the mass of the International Space Station and about the size of the decommissioned Russian Mir space station.
The construction of the station is based on the experience gained from its precursors, Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2 The first module, the Tianhe ("Harmony of the Heavens") core module, was launched on 29 April 2021,[ followed by multiple crewed and uncrewed missions and two more laboratory cabin modules Wentian ("Quest for the Heavens") launched on 24 July 2022 and Mengtian ("Dreaming of the Heavens") launched on 31 October 2022.The research conducted on the station aims to improve researchers' ability to conduct science experiments in space.
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General USA vs China 01-January-2023 by east is risingIn August 2019, Huawei introduced HarmonyOS Operating Syatem. The company's consumer chief Richard Yu said during the announcement that the operating system was designed to work on a variety of devices such as smartphones, smart speakers, automobiles, computers, smart-watches, and tablets. According to GizChina, HarmonyOS Operating System is running on more than 320 million handsets. This operating system is the third largest mobile OS in the world after Android (Google) and iOS (Apple) with an annual growth rate of 113%. Third-party installations of HarmonyOS are also on the rise with over 250 million units of products such as light bulbs, televisions, microwaves, and refrigerators using the software. Those installations are increasing at a rate of 212% on an annual basis. Huawei's own AppGallery app storefront is also growing rapidly and is now the third largest in the world after the Google Play Store and the App Store and serve more than 580 million monthly users.
U.S.A. is making sure that Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines cannot be imported by China. But MyDrivers says that Huawei has recently submitted an application for a patent covering some EUV components and the EUV lithography process. The application number is 202110524685X. EUV machine which is about the size of a school bus. Each EUV machine has over 100,000 components. Huawei's patent reportedly improves some issues inherent in the EUV process by featuring a more uniform light source. Dutch firm ASML, filed a similar patent in 2016. But both patents differ in the way light is used in the EUV. Additionally, Huawei is believed to be working on a way to "bypass" lithography by using optoelectronic wafers and other innovations. If the company can conme up with a way to bypass the lithography process, that would be the time for Samsung and Apple to start worrying.
If Huawei can patent its own EUV technology, China get closer to its goal of becoming self-sufficient in semiconductors. It would also allow Huawei to offer 5G as a native feature on its phones while equipping them with the most powerful and energy-efficient SoCs available
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 27-December-2022 by east is risingUDN says in November, 2022 Huawei has applied for the patent of ultraviolet EUV lithography scanner. Application Number was 202110524685. It covers all crucial components of an EUV scanner including a 13.5 nm EUV light generator (light source), a set of reflecting mirrors, the lithographic system and control management technologies. This will help Chinese chip making companies to produce below 7 nm chips. This is a great victory for China and Huawei against the Semiconductor War unleashed by USA. Dutch EUV scanner maker ASML was forced not to sell EUV to Chinese companies. ASML has to abide by US order as it uses many US technologies in its production line. Moreover, ASML is only company in the world making lithographic EUV scanner. But is has taken financial help from Intel, Micron, HKHynix, Samsung and TSMC. So ASML is bound to give EUV scanner to these companies. But ASML has no obligation to give EUV scanner to any Chinese company. USA used this opportunity and denied ASML EUV scanner to Chinese semiconductor making industry.
Huawei and Chinese Academy of Sciences agreed that making ultraviolet EUV lithography scanner domestically is the key to break US seize of Chinese semiconductor making industry. Huawei is world's biggest cooperative company with USD 100 billion revenue. It set chip production and wafer fab equipment (wfe) production as its primary objectives. Huawei and HiSkey have top notch chip design skills but that is useless without EUV scanner. So Huawei started to invest in EUV scanner production.
Chinese actions soon started giving excellent results. Huazhao Precision Tech developed dual stage system, only second company after ASML to do so. Watching this development ASML warned USA that China will be able to produce EUV scanner in 15 years if the ban continues. But China made more progress in just 1 year. Professor Tang Chuanxiang of Tsinghua University succeeded in exploring a new type of particle accelerator light source "stead state micro bouncing" in February, 2022. This can be used in EUV production as well as in other high tech industries. By August, 2022, Chinese Academy of Sciences has officially completed the installation and application of high energy radiation light source equipment. At the same time, the linear Lloyd lens coating device and nano-focusing lens coating device developed by Zhongke Kemei have also been put into use. These two devices combined with high-radiation light source equipment can almost meet the physical lens technology of all process requirements, including Zeiss lenses.
This means that the three core technologies of EUV lithography machines namely the dual work stage system, the light source and the optical lens have all been broken. But we must remember that filing patent is completely different from actual production because actual production needs to tackle lot of practical problems. Moreover, even with EUV scanner chip making is not possible if there is no pellicle of masks, resists, etc.
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 26-December-2022 by east is risingDespite the US' latest restrictions on exports of advanced-node chips and related manufacturing equipment to China, China will still be capable of developing its homegrown AI chips for edge computing applications, according to industry sources.
Under the restrictions, Chinese foundries are unable to acquire the most advanced chip manufacturing processes and their technology will stay put at the 28nm node; many HPC chip designers fail to import advanced-process wafers; and terminal device makers cannot procure high-end processors from US suppliers such as Nvidia and AMD to develop AI equipment, the sources said.
But if abandoning the development of supercomputer chips or cloud computing chips that require the support of advanced process nodes, and instead focusing on edge AI chips carrying lower process requirements, China will still have a chance to gain a solid presence in the global AI market, the sources stressed.
Actually, Chinese AI-related IC designers have not yet progressed to the development of high-end CPU and GPU chips in recent years. They still mostly focus on mature-process MPU (micro processing unit) and ASIC chips for image processing and security surveillance applications, which will surely become a major segment for the designers to tap deeper, sources continued.
Meanwhile, many AI chips have yet to fully demonstrate their actual computing power due to constraints in software designs, the sources indicated, and therefore upgrading the computing performance of the chips through software enhancement will be a key task for the AI chip design sector in China.
With software breakthroughs, theoretically, the 28nm node will be able to fabricate relatively high-level edge AI chips that can well serve AIoT, automotive electronics and other related applications, the sources emphasized.
In fact, for the vast edge computing market, what AI chips pursue is definitely not the extreme computing power but the optimal cost-effective solution. With its own robust software prowess, China will be able to achieve its self-sufficiency in edge AI chips, the sources remarked.
Jay Liu, Taipei; Willis Ke,
DIGITIMES Asia
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 29-October-2022 by east is risingOn October 7, the US Department of Commerce expanded licensing requirements for exports of advanced semiconductors and the equipment that’s used to make them to cover all shipments to China and not just shipments to particular companies.
The share prices of companies expected to be affected had already dropped, discounting previously announced sanctions and the downturn in the semiconductor cycle that was already underway.
From their 52-week highs to recent 52-week lows:
Intel (INTC) was down 56%;
Micron (MU) was down 50%;
Nvidia (NVDA) was down 69% (its products having been directly targeted by the Biden administration); and
AMD (AMD) (also directly targeted) was down 67%.
Among US semiconductor equipment companies:
Applied Materials (AMAT) was down 57%;
Lam Research (LRCX) was down 59%; and
KLA (KLAC) was down 45%.
Outside the United States, ASML (ASML) of the Netherlands was down 59% from 52-week high to 52-week low. Japanese equipment makers Tokyo Electron (TYO 8035) and Screen Holdings (TYO 7735) were down 50% and 44%, respectively.
Japanese semiconductor makers Renesas (TYO 5723) and Rohm (TYO 6963) were down only 27% and 28%, but they focus on automotive and industrial semiconductors, not the artificial intelligence and high-performance computing devices that obsess the Biden administration. Their 52-week lows were last March.
SMIC (HKG 0981), China’s top IC foundry, was down 40% while TSMC (TPE 2330) was down 43% – a relatively strong performance under the circumstances.
In terms of share price performance and investor returns, American companies and ASML have been hit harder than the Chinese. That might seem ironic considering the measures target China, but it is the market’s discounting mechanism at work.
US government policy is aggravating what was already shaping up to be a severe industry downturn – and friendly fire is a real problem.
On its earnings call on October 13, TSMC announced that it had decided to reduce 2022 capital spending to US$36 billion from about $40 billion due to falling global demand for semiconductors and rising costs.
Management had planned to spend $40 billion to $44 billion this year but said in July that actual spending would be at the bottom of that range. Compared with the $30 billion spent in 2021, projected growth has dropped from a maximum of 47% to 33% and is now 20%.
Mitigating factors for TSMC include a one-year authorization from the US government to continue with the expansion of its facilities in Nanjing and the possibility of a rebound in demand when China’s Covid restrictions are loosened. But TSMC CEO C C Wei also told the media that “We expect probably in 2023 the semiconductor industry will likely decline.”
At the end of September – when announcing results for its fiscal year 2022, which ended on September 1 – US memory chip maker Micron told investors that the company’s capital spending would be cut by a third, from $12 billion to about $8 billion, in the year ahead.
Construction spending should more than double, “to support demand for” the second half of the decade, “but spending on wafer fab production equipment is likely to decline by nearly 50% due to “a much slower ramp of our 1-beta DRAM and 232 layer NAND [the company’s newest and most advanced products] versus prior expectations.”
Furthermore, “To immediately address our inventory situation and reduce supply growth, we are selectively reducing utilization in both DRAM and NAND.” Reports from Micron and its South Korean and Japanese competitors indicate that memory chip production has been cut by about 30%.
Samsung’s approach to capital spending is similar to Micron’s. Its “shell first” strategy is to build clean rooms first so it can install equipment flexibly and rapidly when the time comes. On October 4, Samsung announced plans to launch a 2-nanometer foundry process (matching TSMC) by 2025 and a 1.4-nanometer process by 2027.
As the global economy weakens and US high-end decoupling from China accelerates, the outlook for semiconductor capital spending continues to deteriorate. Last March, market research organization IC Insights forecast a 23.5% increase to $190 billion in calendar 2022.
That industry capital spending figure was reduced to $185.5 billion in August but the announcements from TSMC and Micron point to a sharper decline. Handel Jones, CEO of American consulting firm International Business Strategies, estimates the figure at $160 billion, an increase of only 4% over last year’s $153.9 billion.
IC Insights itself qualified its August forecast, writing that “a menacing cloud of uncertainty looms on the horizon. Soaring inflation and a rapidly decelerating worldwide economy caused semiconductor manufacturers to re-evaluate their aggressive expansion plans at the midpoint of the year. Several (but not all) suppliers – particularly many leading DRAM and flash memory manufacturers – have already announced reductions in their capex budgets for this year.
“Many more suppliers have noted that capital spending cuts are expected in 2023 as the industry digests three years of robust spending and evaluates capacity needs in the face of slowing economic growth.”
When the dot.com bubble burst in 2000, semiconductor capital spending dropped 55% in two years. The Lehman Shock triggered a 57% decline, also over two years. Now, capital expenditure is dropping back from an all-time record high, suggesting a decline of similar magnitude and perhaps duration.
On October 12, The Wall Street Journal reported that US equipment makers including KLA and Lam Research have halted installation and support of equipment at China’s Yangtze Memory Technologies Co (YMTC) while assessing the new US Commerce Department rules. The share price of Japanese NAND flash memory maker Toshiba (TYO 6502), which competes with YMTC, jumped 10% on the news.
YMTC’s NAND flash memory is good enough for Apple and there is no evidence that its technology was stolen, so this can be considered an escalation of US policy from the punishment of bad actors to an all-out attempt to stifle Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing and thus roll back the development of China’s economy.
Commencing immediately, the withdrawal of American support staff will crimp Chinese semiconductor production.
In addition, a new Commerce Department regulation that “restricts the ability of US persons to support the development, or production, of ICs at certain PRC-located semiconductor fabrication ‘facilities’ without a license” is already disrupting the operations of Chinese companies.
By forcing numerous executives and engineers of Chinese extraction to choose sides, it brings decoupling down to the personal level.
Data from Tokyo Electron show the company’s total sales of semiconductor production equipment up 2.6 times in the five years to March 2022 (the company’s fiscal year ends in March). The increase was led by a 5.7x increase in China, which grew from 12% to 26% of total sales.
In the two years to March 2022 alone, sales in China increased by 2.7x. That suggests that the Chinese semiconductor industry has purchased enough equipment to see it through the next two or three years, at least.
Tokyo Electron’s performance in other regional markets was not exceptional. Sales were up 2.7x in Korea, 2.6x in the US, 2.5x in Japan, 1.8x in Europe, 1.6x in Taiwan (which started at a high level), and 2.1x in Southeast Asia and other regions.
As Japan’s largest and the world’s third-largest maker of semiconductor production equipment, with a diversified product portfolio, Tokyo Electron is representative of the industry as a whole.
The Chinese can no longer rely on US equipment suppliers and European and Japanese suppliers must follow US rules if their products incorporate US technology, so China will step up its import substitution campaign.
Sanctions on China have already caused large losses for American semiconductor and equipment companies, and more are probably on the way. Furthermore, in the next up-cycle, the China opportunity for foreign suppliers is likely to be much diminished.
Follow this writer on Twitter: @ScottFo83517667
Read MoreAuthor: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General 19-October-2022 by east is risingঅষ্টাদশ ও ঊনবিংশ শতাব্দীতে যান্ত্রিক সভ্যতার অগ্রগতির সাথে সাথে সারা বিশ্বে রাবারের চাহিদা বেড়ে যায়। বৈদ্যুতিক তারের ইনসুলেশন , সাইকেল ও গাড়ির টায়ার যুদ্ধাস্ত্র ও ভারী যন্ত্রপাতি তৈরি করতে রাবারের প্রয়োজন হতো। কয়েক টুকরা রাবারের অভাবে অনেক সময় ভারী যন্ত্রপাতির উৎপাদন আটকে যেত।
সিন্থেটিক রাবার আবিষ্কারের আগে বৈশ্বিক চাহিদার বেশিরভাগ পূরণ হতো আমাজন জঙ্গলের রাবার গাছ থেকে। একক পরাশক্তি হিসেবে বৃটেনের রাবারের চাহিদা ছিল অনেক বেশি। রাবারের গুরুত্ব বুঝতে পেরে ব্রিটেন সিদ্ধান্ত নেয় রাবার উৎপাদনের উপর নিজের নিয়ন্ত্রন স্থাপনের।
এই উদ্দেশ্যের লন্ডনের রয়েল বোটানিকাল ইনস্টিটিউট 1876 সালে হেনরী উইকহ্যাম নামে এক ব্রিটিশ পর্যটককে দায়িত্ব দিয়ে আমাজনে পাঠায়। নৌকা নিয়ে আমাজনের গভীরে ঢোকার পর তিনি পায়ে হেঁটে যেখানে সবচেয়ে ভালো রাবার গাছ জন্মায় সেখানে পৌঁছান।
তিনি স্থানীয় অধিবাসীদের অর্থের লোভ দেখিয়ে হাতে বোনা ঝুড়িতে রাবার বীজ সংগ্রহ করতে থাকেন। সমুদ্রে দীর্ঘযাত্রার ধাক্কা এড়াতে ঝুড়িগুলোকে কয়েক স্তরের কলাপাতা দিয়ে মুড়িয়ে নেওয়া হয়।
এভাবে প্রায় 70,000 বীজ নিয়ে তিনি বৃটেনের উদ্দেশ্যে রওনা হন। ভিন্ন নামে একটি ট্রেডিং লাইসেন্স ব্যবহার করে ও বীজগুলিকে একাডেমিক স্যাম্পল ঘোষণা দিয়ে তিনি স্থানীয় কর্তৃপক্ষের নজর এড়াতে সক্ষম হন।
দীর্ঘযাত্রার ধকল পেরিয়ে লন্ডনে পৌঁছানোর পর মাত্র 2,700 বীজ অঙ্কুরোদগমের উপযোগী পাওয়া যায়। একটা পরিকল্পিত প্লান্টেশন শুরু করার জন্য এই পরিমাণ বীজ যথেষ্ঠ ছিল। চারাগুলিকে পরে বিভিন্ন ব্রিটিশ কলোনি যেমন মালয়েশিয়া , শ্রীলংকা , বাটাভিয়া , ট্রপিক্যাল আফ্রিকায় পাঠানো হয়।
এশিয়ার পরিবেশে চারাগুলি বেশ ভালোভাবেই বেড়ে ওঠে এবং আমাজনের মূল গাছ থেকে বেশি পরিমাণ রাবার দিতে থাকে। এই রাবার বাজারে আসার পর ধীরে ধীরে আমাজনের রাবার বাজার দখল করে ফেলে।
জঙ্গল থেকে রাবার সংগ্রহ করা ব্যয়বহুল হওয়ায় আমাজনের রাবার কেন্দ্রিক শহরগুলি আস্তে আস্তে মৃত শহরে পরিণত হয়। ধীরে ধীরে রাবার বাজারের উপর বৃটেনের একচেটিয়া নিয়ন্ত্রণ প্রতিষ্ঠা হয়।
এই কৃতিত্বের পুরস্কার স্বরূপ রানী ভিক্টোরিয়া হেনরী উইকহ্যামকে নাইট উপাধিতে ভূষিত করেন। এই রোমাঞ্চকর ঘটনাটি নিয়ে জো জ্যাকসন নামে একজন লেখক পরে ''The Thief at the End of the World: Rubber, Power, and the Seeds of Empire '' একটি বিখ্যাত বই লেখেন।
বিশ্বে বায়ো পাইরেসির ঘটনা এটাই প্রথম নয়। এর আগে চীন থেকে পরিকল্পিতভাবে রেশম পোকা চুরি করে নিয়ে যাওয়া হয়। ব্রিটিশরা চীনের একচেটিয়া চায়ের বাজার দখল করার জন্য চীন থেকে চায়ের গাছ জোগাড় করে ভারতবর্ষে পরীক্ষা করেছিল।
বাউন্টিতে বিদ্রোহ বইটি পড়লে বা মুভি দেখে থাকলে জানবেন যে ব্রিটিশরা পলিনেশিয়া থেকে রুটি ফলের চারা নিয়ে যাচ্ছিল ওয়েস্ট ইন্ডিজে চাষাবাদের জন্য।
Read MoreAuthor: Ahmed Rafique Barki
Technology news General 15-October-2022 by east is risingWatch out the video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dnHdqPBrtH8
USSR could not use scale of global market. It means USSR was mere 10% of global economy while USA was 35% of global economy and USA could trade with West Europe and Japan who made another 25% of global economy which USSR could not. USSR traded mainly with East Europe who make 5% of global economy. Third World have only raw materials and no technology to trade with.
USSR could not use individual entrepreneurship and so failed to commercialize the technologies invested by USSR scientists. USSR was number one in patent making from 1960 to 1985. In USSR technological demand mainly used to come from military and little from from production.
USSR shows central planning is best for Research and Inventions and market is best for commercializing those inventions. Thus USSR could easily compete with USA in technologies but not in production and the more USSR lost in production the more its competitive edge in technology is lost.
Low fertility rate (less than replacement rate of 2.1) since 1970s further weakened production base of USSR as it could not rely on rise in productivity and efficiency of workers which is considered exploitation due to flawed understanding of Marxism. USSR growth was dependent on growth of population and since 1970s this only growth factor was gone.
In 1970s, it seems USSR was winning mainly due to rise of anti colonial movements across the Third World and USA's non intervention approach due to Kissinger's decolonisation policy after loss of Vietnam War. Also high inflation in global market made USSR economic condition look good and its non integration to global economy was given credit.
In 1970s, USSR economy looked in good shape due to high oil price. Many of USSR problems were neglected in 1970s due to the fact that oil exports was leading to huge foreign exchange gains. In fact, this high oil price further weakened production base of USSR.
In 1980s when oil price went down, USSR understood its production base was gone. Population growth has stopped and so production growth has to rely on productivity gains only. So reforms had to start which was looked down upon as anti Marxist again due to lawed understanding of Marxism.
Global market in 1980s is facing low inflation rate due to lower oil price and becaue of integration of huge Chinese productive cheap labor force into the global economy.
It is said that Marxists are masters of using rivalry among capitalists for their own gains. Lenin used German vs British to form USSR. Stalin used American British rivalry with German Japanese to make USSR a super power. But Breznev failed to use the capitalist rivalry between UK based computer maker ICL and US based counterpart IBM. Gorbachev failed to use Japanese offer for help to counter US competitors. Toshiba, the Japanese chip maker tried to help USSR chip making but Gorbachev failed to use the offer. In fact, Toshiba was punished severely by US government for offering help to USSR.
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news General Socialism Communism Xi Jinping Mao USSR China 12-July-2022 by east is risingAll Bengal Men's Forum-এর প্রধান নিন্দিনী ভট্টচারয-কে উৎসর্গ করে এই লেখা লিখলাম।
এক উনি আমাকে উৎসাহিত করেছেন পুরুষাধিকার নিয়ে লিখতে।দুই উনি সমস্ত পুরুষাধিকার সংগঠনগুলোকে নিয়ে একটা অনুষ্ঠানের আয়োজন করেন ১৮ই জুন, ২০২২ ICCR এ। সেখানে আমার দেখা হয় পশ্চীম বঙ্গের প্রথম একক পালক পিতার (Foster Father) সঙ্গে যিনি একক পালক পিতা হওয়ার প্রক্রিয়াটা তুলে ধরেন। আমি তার কাছ থেকে আলাদা করে একক পালক পিতা হওয়ার প্রক্রিয়ার খরচও জানি (১১ লাখ টাকা)।
তারপরেই আমার অনেকদিনের একটা সমস্যা দূর হয়। সমস্যাটা হল স্বল্প জন্মহারের সমস্যা আগামীদিনে মানব সভ্যতা কিভাবে মোকাবিলা করবে। পুরুষাধিকার আন্দোলনে আমার আসা এই সমস্যা দূর করার ইচ্ছা থেকেই। একক পালক পিতা হওয়ার প্রক্রিয়াটা জেনে প্রথম আমি স্বল্প জন্মহার সমস্যা দূর করার একটা উপায় আবিষ্কার করি। এই আবিষ্কার করে আমার ভাল লাগছে এবং আবারও বলি নন্দিনীদির জন্যেই আমি চীন থেকে ফিরে আবারও পুরুষাধিকার আন্দোলনে আসি এবং ওনার জন্যেই অভিষেক বাবুর সঙ্গে আমার দেখা হয়। ওনাদের দুজনের কাছেই আমি ঋণী।
পুরুষের পক্ষে বিয়ে যে বর্তমানে লাভজনক প্রতিষ্ঠান নয় তা এখন পুরুষাধিকার আন্দোলনের সঙ্গে যুক্ত লোকেরা সবাই জানে আর মানে। কেউ চাইছে আইন বদলে বিয়েকে পুনরায় পুরুষের কাছে লাভজনক করতে আর কেউ বলছে আইন বদলালো কি না ভেবে লাভ নেই, বিয়ে/প্রেম এড়িয়ে গিয়ে জীবনকে উপভোগ কর। যৌন ক্রিয়া অন্যন্য অনেক উপভোগ্য ক্রিয়ার মধ্যে একটা। তাই যৌন পরিষেবা যাতে বাজার থেকে বিনা বাঁধায় কেনা-বেচা করা যায় তার পক্ষে বলবে পুরুষাধিকার আন্দোলোনের সাথে যুক্ত সকলেই। কিন্তু যৌনতার উপভোগ্য পরিষেবা ছাড়াও আরেকটা উপযোগিতা আছে। আর তা হল সন্তানলাভ। বাজার থেকে যৌন পরিষেবা কিনলেই সন্তানলাভ করা যাবেনা। সন্তানলাভ করতে গেলে দীর্ঘ ১০ মাস ১০ দিন ধরে গর্ভ থেকে ভ্রুণ যে পরিষেবা পায় তা নিশ্চিত করতে হবে।
এই গর্ভের পরিষেবা যৌন পরিষেবার থেকে সম্পূর্ণ আলাদা। একজন পুরুষের শুক্রাণু ও একজন নারীর ডিম্বাণু নিয়ে দ্বিতীয় আরেকজন নারীর কাছ থেকে গর্ভ পরিষেবা নেওয়া যেতে পারে প্রযুক্তির মাধ্যমে। পুরুষাধিকার আন্দোলনকে শুক্রাণুর বাজার, ডিম্বাণুর বাজার এবং গর্ভ পরিষেবার বাজারকে উন্মুক্ত করার পক্ষে থাকতে হবে। কিছু পুরুষের শুক্রাণুর বাজার দর বেশি হবে, কিছু পুরুষের শুক্রাণুর বাজার দর কম হবে। কিছু নারীর ডিম্বানুর বাজার দর বেশি হবে, কিছু নারীর ডিম্বানুর বাজার দর কম হবে। আবার কিছু নারী গর্ভ পরিষেবা দিতে রাজি থাকবে। চীনে আর্টিফিশিয়াল ইন্টেলিজেন্স ব্যবহার করে এখন আরটিফিসিয়াল গর্ভ তৈরি করা হয়েছে, যদিও তা অনেক খরচ সাপেক্ষ। কিন্তু বিজ্ঞান ও বাজারের চাপে আশা করা যায় ক্রমেই আরটিফিসিয়াল গর্ভ সাধারণ মানুষের সাধ্যের মধ্যে বলে আসবে। তা এসে গেলে নারীর কাছ থেকে গর্ভ পরিষেবা পাওয়ার দরকার হবেনা।
এটা মনে রাখা দরকার যে একজন নারী জন্মায় ১০ লক্ষ ডিম্বাণু নিয়ে, কিন্তু সেই নারী যখন বয়ঃসন্ধি কালে পৌঁছয় তখন তার মাত্র ৩০,০০০ হাজার ডীম্বাণু বাকি থাকে। এদের মধ্যে ৩০০-৪০০ ডিম্বাণু প্রজনন কালে সন্তান দেওয়ার উপযোগী থাকে। যত বয়স বাড়বে নারীর ডিম্বাণুর মান কমতে শুরু করবে। বিয়ে/প্রেম/সহবাস ইত্যাদির মতো প্রতিষ্ঠানে হয় একজন নারীকে অল্প বয়সে বাচ্চা নিতে হবে নয়তো বেশি বয়সে বাচ্চা নিতে হবে যখন ডিম্বানুর মান যথেষ্ট খারাপ হয়ে গেছে। বর্তমান যুগে নারী যেহেতু পড়াশুনা করে চাকরী করছে, তাই বিয়ের বয়স বেড়ে যাচ্ছে এবং খারাপ মানের ডিম্বানু জাত সন্তান আসছে পৃথিবীতে। কিন্তু ডিম্বানুর যদি পর্যাপ্ত বাজার থাকে, তাহলে অল্প বয়সে নারীরা তাদের উচ্চমানের ডিম্বানু বাজারে বিক্রি করতে পারবে যা ব্যবহার করে ডিম্বানুর ক্রেতা পুরুষ নিজের সন্তানলাভ করবে। ডিম্বানু বিক্রেতা নারীটি এই ক্ষেত্রে নিজের গর্ভে সন্তান নাই নিতে পারে এবং ডিম্বানু ক্রেতা পুরুষ গর্ভের পরিষেবা পেতে দ্বিতীয় কোন নারীর গর্ভ পরিষেবা কিনতে পারে। আরও উল্লেখযোগ্য বিষয় হল, বিয়ে/প্রেম/সহবাস ইত্যাদির মতো প্রতিষ্ঠানে যেই সকল নারীর SMV বা যৌন বাজার মূল্য অত্যন্ত বেশি, সাধারণ পুরুষ তাদের ডিম্বানুজাত সন্তান চাইলেও পাবেনা। কারণ উচ্চ SMVএর নারী প্রজননকালে খুব বেশি বিয়ে করতে পারবেনা এবং সন্তানও নেবে সীমিত সংখ্যায়। বরোজোড় ৩টে। তাও প্রজনন কালের শেষের দিকে। বাকি ২৯৭-৩৯৭ ডিম্বাণু সম্পূর্ণ নষ্ট হবে। ডিম্বাণুর বাজার উন্মুক্ত হলে উচ্চ SMVএর নারীর বাকি ২৯৭-৩৯৭ ডিম্বাণু অল্প বয়সেই সন্তান দেওয়ানোতে ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে। আর ওই সময় নারীটি তার পছন্দ মতো কাজও করতে পারবে গর্ভে কোন সন্তান না নিয়েই। যেখানে উচ্চ SMVএর নারীর থেকে সমাজ ৩টে সন্তান পাচ্ছিল এখন সমাজ তার থেকে ৩০০-৪০০ সন্তান পেতে পারে কারণ উচ্চ SMVএর নারীর ডিম্বানুর যথেষ্ট পরিমাণে পুরুষ ক্রেতা থাকবে।
পুরুষ ১৪ থেকে ৬৫ বছর পর্যন্ত শুক্রাণু তৈরিতে সক্ষম। পুরুষ তার পুরো বয়স ব্যবহার করে পর্যাপ্ত অর্থ উপার্জন করে মনের মতো ডিম্বাণু কিনে সময় মতো সন্তান নিতে পারে। নারীরাও উচ্চ SMV-এর পুরুষের শুক্রাণু কিনে নির্দিষ্ট বয়সে পৌঁছে সন্তান নিতে পারবে। সমস্যা এখানেই যে যেসকল নারী নিজেদের গর্ভ পরিষেবা বাজারে বিক্রি করবে তারা অর্থনৈতিকভাবে দুর্বল হলেই কেবল এমন কাজ করবে। তাই উন্নয়ন যত হবে, মানুষ অর্থনৈতিকভাবে স্বাধীন হবে, এমন নারী পাওয়া কঠিন হবে যে নিজের গর্ভ পরিষেবা বাজারে বিক্রি করবে। তাই গর্ভ পরিষেবা যত তাড়াতাড়ি সম্ভব স্বয়ংক্রিয় করার পক্ষে আমি। অর্থাৎ সাধারণ মানুষের জন্য আরটিফিসিয়াল গর্ভ যত তাড়াতাড়ি সম্ভব উদ্ভাবন করতে হবে। কিন্তু এও মনে রাখতে হবে যে গর্ভ পরিষেবা বিক্রেতা তার অল্প বয়সেই যদি এই কাজ শুরু করে তবে ১৫ বছরে (২০ থেকে ৩৫ বছরের মধ্যে) ৭টি সন্তান দিয়ে সে যথেষ্ট রোজগার করে নিক যাতে বাকি জীবনটা তার ভালভাবে কেটে যায়। সরকার এক্ষেত্রে গর্ভ পরিষেবার বাজার মূল্য নির্দিষ্ট করে দিতেই পারে। তাহলে বহু নারী এই পরিষেবা দিতে উৎসাহ বোধ করবে।
শুক্রাণু, ডিম্বাণু ও গর্ভ পরিষেবার বাজার উন্মুক্তকরণ ভিষণভাবেই পালটে দেবে দুনিয়া। জনসংখ্যা একই রেখে দিতে যে কোন সমাজের সমস্ত নারীকে ২টো সন্তান জন্ম দিতে হবে। অনাকাঙ্ক্ষিত মৃত্যু ও প্রজনন সমস্যার জন্য আমরা আনুমান করি যে ২.১ সন্তানের জন্ম গড়ে সমাজে সমস্ত নারীকে দিতেই হবে। বিয়ে/প্রেম/সহবাস ইত্যাদির মতো প্রতিষ্ঠান বর্তমান অর্থনীতির সঙ্গে মানানসই নয়। একজন নারী নিজের পায়ে দাঁড়াতে গিয়ে তার শ্রেষ্ঠ সময়টায় সন্তান নিতে পারছেনা। নারীরা বেশি বয়সে বিয়ে করার কথা ভাবছে বলে পুরুষরাও বিয়ের জন্য পছন্দসই নারী পাচ্ছেনা। পেলেও কোন মতে একটা সন্তান নিচ্ছে। আমরা যদি শুক্রাণু, ডিম্বাণু ও গর্ভ পরিষেবার বাজার তৈরি করতে পারি তবে গর্ভ পরিষেবা বিক্রেতা নারীরা গড়ে ৭টা শিশুর জন্ম দিতে পারবে গর্ভ পরিষেবা দিয়ে। এর ফলে সমাজের মোট নারী সংখ্যার স্রেফ ৩০% (২.১/৭=০.৩=৩০%) নারীকে সমাজের প্রয়োজন হবে গর্ভে সন্তান ধারণ করতে। বাকি ৭০% নারী সমাজের অন্যান্য কাজে পুরো সময় দিতে পারবে। এভাবনে জনসংখ্যা পতন রোধ করা সম্ভব হবে।
১০০% পুরুষ ও ১০০% নারী তার আকাঙ্ক্ষিত মানুষের থেকে তার সন্তান পেয়ে যাবে, তারা পুরো সময়টা সে দিতে পারবে তাদের কর্মক্ষেত্রে ও জীবনকে উপভোগ করাতে। তারা পর্যাপ্ত রোজগার করে ও সঠিক বয়সে এসে তবেই সন্তানকে লালন পালন করবে। আরেকটা বিষয় হল সকল পুরুষ ও নারী গড়ে একজন করে সন্তানের লালন করলেই সমাজ জনসংখ্যা পতন রোধ করতে পারবে। আগামী দিনের স্বল্প জন্মহারের সমস্যা থেকে মুক্তি পেতে বিয়ে/প্রেম/সহবাস ইত্যাদির মতো প্রতিষ্ঠানের ওপর নির্ভরতা কমাতে হবে এবং শুক্রাণু, ডিম্বানু ও গর্ভ পরিষেবার বাজারকে উন্মুক্ত করতেন হবে। এটা করলে জনসংখ্যা হ্রাস তো আটকানো যাবেই, এমনকি সমস্ত মানুষ তার আকাঙ্ক্ষিত মানুষের থেকে সন্তানলাভ করতে পারবে পর্যাপ্ত অর্থ থাকলেই। ফলে মানুষ অনেক বেশি অর্থ উপার্জনের জন্য অনুপ্রাণিত হবে এবং এর ফলে অনেক বেশি কর্মোদ্যোগী হবে। আবার জীবনের সবচেয়ে বেশি কর্মক্ষম সময়টুকু নিজের কর্মে নিয়োজিত করতে পারবে। আবার জীবনকে উপভোগ করার মতো পর্যাপ্ত সময়ও পাবে। আবার সমাজে সমস্ত জীন বেঁচে থাকবে এবং সমাজে জীনের তারতম্য বজায় থাকবে। সবার ওপরে একজন মানুষ গড়ে একজন সন্তানকে বড়ো করার দিকেই মন দিতে পারবে।
তবে মনে রাখতে হবে এই সুন্দর সমাজ তৈরি করতে গেলে নারী ও পুরুষকে সমান চোখে দেখতে হবে। একজন পুরুষকে সমাজ ও আইন যদি তার সন্তানকে বড় করার অধিকার দেয় তাহলে নারীরাও কিন্তু একাধিক সন্তানকে বড় করার দায় থেকে মুক্তি পাবে। নারীরা আজ চাকরীতে যায়, আগের মতো পুরো সময় সন্তানকে দিতে পারেনা। একাধিক সন্তানকে বড় করা তার পক্ষে আরও কঠিন হয়ে দাঁড়ায়। তাই নারী বাধ্য হয় একের বেশি সন্তান না নিতে এবং অনেক ক্ষেত্রে একমাত্র সন্তানকে কোন পেশাদার আয়ার কাছে বা ক্রেশে সন্তানকে রেখে যেতে। আইন ও সমাজ যদি পুরুষের ওপর তার নিজের সন্তানের ভার ছাড়ে তাহলে পুরুষও পেশাদার আয়া ও ক্রেশের সাহায্য নিয়ে এক বা একাধিক সন্তানকে বড় করতেই পারে। সমাজ ও আইন পুরুষের ওপর পিতা হিসেবে ভরসা করতে পারলে সমাজ ও নারী উভয়েরই লাভ হবে।
আমি আবারও বলব গর্ভ পরিষেবা বিক্রেতাকে যেন সমাজ ও আইন অর্থনৈতিক ও সামাজিক সুরক্ষা দেয়। মোট নারী সংখ্যার ৩০%-কে আমরা গর্ভ পরিষেবা বিক্রেতা বানাতে পারলেই আমাদের সমস্যা অনেক দূর হবে। সেই জন্য গর্ভ পরিষেবার বাজারকে বিক্রেতার কাছে লাভজনক করে তোলা খুবই দরকার। তারা যেন কোনভাবেই তাদের অর্থনৈতিক দুর্বলতার জন্য বঞ্চিত না হয়। তারা বঞ্চিত হলে আমাদের পুরো প্রকল্প ব্যর্থ হবে।
নারী ও পুরুষ সমাজে একে অপরের পরিপূরক। একজনের ওপর ভরসা বাড়ালে আরেকজনের বোঝা খানিকটা কমবে। নারী আজ রোজগার করছে বলে, পুরুষের ওপর অর্থনৈতিক চাপ কমেছে, পুরুষের সন্তান পালনের ওপর ভরসা করতে পারলেও নারীর ওপর সন্তান পালনের চাপ কমবে। তবে ভরসা করতে হবে স্বাধীন পুরুষ ও স্বাধীন নারীকে। স্বামী-স্ত্রী বা প্রেমিক-প্রেমিকা হিসেবে আরে পুরুষ ও নারী একে অপরের পাশে দাঁড়াতে পারবেনা। তাই অবিবাহিত পুরুষকে নিজের ঔরসজাত সন্তানের একক পালক পিতা (single foster father) হওয়ার অধিকার এখনই দেওয়া প্রয়োজন। মানব সভ্যতার ভবিষ্যৎ বিয়ে/প্রেমসহবাস নয়। মানব সভ্যতার ভবিষ্যৎ হল শুক্রাণু, ডিম্বাণু ও গর্ভ পরিষেবার বাজারকে উন্মুক্ত করায়। আশা রাখি একদিন স্বয়ংক্রিয় আরটিফিসিয়াল গর্ভ ও যৌন রোবট আসবে এবং আমাদের জীবনকে আরও সুন্দর করবে।
প্রথমে এই বাজার কেবল উচ্চবিত্ত ও উচ্চ মধ্যবিত্তদের মধ্যে সীমাবদ্ধ থাকবে কিন্তু ক্রমেই মুনাফা ও সামাজিক প্রয়োজনে অন্যান্য সমস্ত বাজারের মতো তা সাধারণ মানুষের কাছেও সুলভ হবে।
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya
Technology news Sex War 28-June-2022 by east is rising