


Uyghur Bookshelf
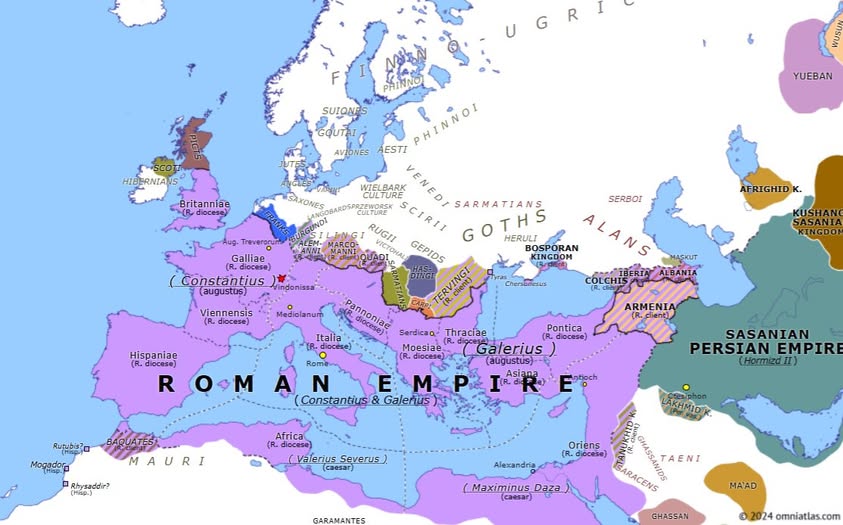
305 A.D. marked a pivotal moment in European history during the late Roman Empire. This was the era of the Tetrarchy, a system of rule established by Emperor Diocletian to stabilize and manage the vast Roman Empire. Here’s an overview of Europe during this time:
________________________________________
1. The Roman Empire
• Tetrarchy:
o The empire was divided into Eastern and Western halves, each governed by an Augustus (senior emperor) and a Caesar (junior emperor).
o In 305 A.D., Diocletian (Eastern Augustus) and Maximian (Western Augustus) abdicated, passing power to their Caesars:
Galerius became Augustus of the East.
Constantius Chlorus became Augustus of the West.
Two new Caesars were appointed: Maximinus Daza (East) and Severus II (West).
• Territory:
o The Roman Empire stretched across most of Europe, North Africa, and parts of the Middle East.
o The Rhine and Danube rivers marked the northern boundaries, constantly threatened by barbarian tribes.
________________________________________
2. Barbarian Tribes and Beyond the Empire
• Germanic Tribes:
o Various Germanic tribes, such as the Goths, Franks, Vandals, and Alamanni, lived beyond the Roman frontiers.
o These tribes occasionally raided Roman territories or were recruited into Roman military service as foederati (allied tribes).
• Huns:
o The Huns, a nomadic people from Central Asia, began moving westward. While their impact on Europe would intensify later, they were starting to displace other tribes, like the Goths.
________________________________________
3. Christianity and Religious Change
• Christianity:
o Christianity was spreading across the Roman Empire despite ongoing persecution.
o The Diocletianic Persecution (303–311 A.D.), the empire's last and most severe campaign against Christians, was ongoing.
o Many Christians became martyrs, further strengthening the religion’s influence.
________________________________________
4. Britain
• Roman Britain:
o Britain was a Roman province under the rule of Constantius Chlorus.
o The island was relatively stable but faced pressure from Picts in the north.
________________________________________
5. Other Key Regions in Europe
• Scandinavia:
o Populated by early Germanic and Norse tribes, not yet centralized into kingdoms.
• Eastern Europe:
o Dominated by migrating peoples, including Slavic and Sarmatian tribes.
• Celtic Regions:
o Celtic culture persisted in areas like Ireland and parts of Scotland, where Roman influence did not reach.
________________________________________
Legacy of 305 A.D.
• The Tetrarchy was an ambitious system to manage the vast Roman Empire, but it eventually collapsed due to internal conflicts and power struggles, leading to Constantine the Great's rise.
• This period set the stage for the Constantinian shift, where Christianity would gain imperial support and transform European history.
Author: Saikat Bhattacharya